Wednesday, August 04, 2010
Sekadau Consensus: Community Mapping in West Kalimantan, Indonesia
The documentary describes a process wherein the Dayak communities in Nanga Mahap, Sekadau District of Indonesia get control and manage their territories and succeed in stopping the expansion of palm oil plantations.
Participatory mapping and spatial planning were used to build new consensus between the communities and the local government at village and sub-District and District level.
The new consensus was built after the communities gained a clearer understanding on the impact of the industrial palm oil plantations on land tenure and on the cultural, economic and ecological sustainability of their villages.
Video and description courtesy Kasmita Widodo, Jaringan Kerja Pemetaan Partisipatif (JKPP).
PCSD endorsement to Macroasia multi-billion giant deferred: an initial victory for NGOs and indigenous peoples
Puerto Princesa - ALDAW - On July 30, over 20 members of the Palawan Council for Sustainable Development (PCSD) - a local government body in charge of the protection and sustainable management of the Province meet to decide whether to issue a SEP (Strategic Environmental Plan) clearance to the mining operations of MacroAsia Corporation (MAC for brevity) with reference to a 91ha area, out of the approved Mineral Production Sharing Agreement area of over 1300 hectares.
 The area for which SEP clearance is being sought consists of well-conserved forest which provides clean water to lowland communities and which is also part of the traditional territory of Palawan tribes living in Brooke’s Point Municipality. During the last PCSD meeting, thanks to the support of Atty Grizelda Mayo-Anda (representing the NGOs community within the Council) and through the effective mediation of Governor Abraham Kahlil Mitra, the ALDAW network (Ancestral Land Domain Watch) was allowed to present ‘geotagged’ findings collected in two separate field surveys carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent (UK). In a photographic context, geotagging is the process of associating photos with specific geographic locations using GPS coordinates. GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of a professional device connected to the camera’s hot shoe during the entire mission’s reconnaissance in the hinterlands of Ipilan and Maasin (Brooke’s Point Municipality). The obtained GPS coordinates were later overlaid on PCSD maps to show the overlapping between core zones and MAC mining activities. Overall the findings indicates that: 1) over 95% of test pits and drilling holes in MAC MPSA area are located in “core zones” and biodiversity rich forest, 2) Isolated Indigenous communities are living in the MPSA area of MAC (these have never been consulted about MAC operations); 3) The 91ha for which SEP clearance is being sought by MAC (out of a total MPSA area of more than 1,300 ha) overlap partially with “core zones” and entirely with well-conserved and residual forest. Even more surprisingly, the mission found no evidence of test pits and drilling holes in the recommended 91ha area. “This area includes sacred places where our Palawan indigenous communities carry out their own rituals. Moreover, portions of the Ipilan river and other tributaries which provide potable and irrigation waters to the lowland farmers are also found inside the area” explained ALDAW Chairman Artiso Mandawa.
The area for which SEP clearance is being sought consists of well-conserved forest which provides clean water to lowland communities and which is also part of the traditional territory of Palawan tribes living in Brooke’s Point Municipality. During the last PCSD meeting, thanks to the support of Atty Grizelda Mayo-Anda (representing the NGOs community within the Council) and through the effective mediation of Governor Abraham Kahlil Mitra, the ALDAW network (Ancestral Land Domain Watch) was allowed to present ‘geotagged’ findings collected in two separate field surveys carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent (UK). In a photographic context, geotagging is the process of associating photos with specific geographic locations using GPS coordinates. GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of a professional device connected to the camera’s hot shoe during the entire mission’s reconnaissance in the hinterlands of Ipilan and Maasin (Brooke’s Point Municipality). The obtained GPS coordinates were later overlaid on PCSD maps to show the overlapping between core zones and MAC mining activities. Overall the findings indicates that: 1) over 95% of test pits and drilling holes in MAC MPSA area are located in “core zones” and biodiversity rich forest, 2) Isolated Indigenous communities are living in the MPSA area of MAC (these have never been consulted about MAC operations); 3) The 91ha for which SEP clearance is being sought by MAC (out of a total MPSA area of more than 1,300 ha) overlap partially with “core zones” and entirely with well-conserved and residual forest. Even more surprisingly, the mission found no evidence of test pits and drilling holes in the recommended 91ha area. “This area includes sacred places where our Palawan indigenous communities carry out their own rituals. Moreover, portions of the Ipilan river and other tributaries which provide potable and irrigation waters to the lowland farmers are also found inside the area” explained ALDAW Chairman Artiso Mandawa.
 The area for which SEP clearance is being sought consists of well-conserved forest which provides clean water to lowland communities and which is also part of the traditional territory of Palawan tribes living in Brooke’s Point Municipality. During the last PCSD meeting, thanks to the support of Atty Grizelda Mayo-Anda (representing the NGOs community within the Council) and through the effective mediation of Governor Abraham Kahlil Mitra, the ALDAW network (Ancestral Land Domain Watch) was allowed to present ‘geotagged’ findings collected in two separate field surveys carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent (UK). In a photographic context, geotagging is the process of associating photos with specific geographic locations using GPS coordinates. GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of a professional device connected to the camera’s hot shoe during the entire mission’s reconnaissance in the hinterlands of Ipilan and Maasin (Brooke’s Point Municipality). The obtained GPS coordinates were later overlaid on PCSD maps to show the overlapping between core zones and MAC mining activities. Overall the findings indicates that: 1) over 95% of test pits and drilling holes in MAC MPSA area are located in “core zones” and biodiversity rich forest, 2) Isolated Indigenous communities are living in the MPSA area of MAC (these have never been consulted about MAC operations); 3) The 91ha for which SEP clearance is being sought by MAC (out of a total MPSA area of more than 1,300 ha) overlap partially with “core zones” and entirely with well-conserved and residual forest. Even more surprisingly, the mission found no evidence of test pits and drilling holes in the recommended 91ha area. “This area includes sacred places where our Palawan indigenous communities carry out their own rituals. Moreover, portions of the Ipilan river and other tributaries which provide potable and irrigation waters to the lowland farmers are also found inside the area” explained ALDAW Chairman Artiso Mandawa.
The area for which SEP clearance is being sought consists of well-conserved forest which provides clean water to lowland communities and which is also part of the traditional territory of Palawan tribes living in Brooke’s Point Municipality. During the last PCSD meeting, thanks to the support of Atty Grizelda Mayo-Anda (representing the NGOs community within the Council) and through the effective mediation of Governor Abraham Kahlil Mitra, the ALDAW network (Ancestral Land Domain Watch) was allowed to present ‘geotagged’ findings collected in two separate field surveys carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent (UK). In a photographic context, geotagging is the process of associating photos with specific geographic locations using GPS coordinates. GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of a professional device connected to the camera’s hot shoe during the entire mission’s reconnaissance in the hinterlands of Ipilan and Maasin (Brooke’s Point Municipality). The obtained GPS coordinates were later overlaid on PCSD maps to show the overlapping between core zones and MAC mining activities. Overall the findings indicates that: 1) over 95% of test pits and drilling holes in MAC MPSA area are located in “core zones” and biodiversity rich forest, 2) Isolated Indigenous communities are living in the MPSA area of MAC (these have never been consulted about MAC operations); 3) The 91ha for which SEP clearance is being sought by MAC (out of a total MPSA area of more than 1,300 ha) overlap partially with “core zones” and entirely with well-conserved and residual forest. Even more surprisingly, the mission found no evidence of test pits and drilling holes in the recommended 91ha area. “This area includes sacred places where our Palawan indigenous communities carry out their own rituals. Moreover, portions of the Ipilan river and other tributaries which provide potable and irrigation waters to the lowland farmers are also found inside the area” explained ALDAW Chairman Artiso Mandawa. In a nutshell the joint ALDAW/CBCD presentation clearly demonstrates that MAC mining interests are really concentrated in primary virgin forest. Geotagged photos portray test pits and drilling holes, found around 800m and even above 1,000m ASL. These evidences generated a lively debate amongst PCSD council members. PCSD representative/Congressman Antonio C. Alvarez asked confirmation to MacroAsia spokesman on whether their explorations activities are really located in core zones of “maximum protection”. To the surprise of all participants, MACROASIA representatives did not deny but rather confirmed the evidences brought forward by the ALDAW investigation team. However, they also stated that their permit to explore in ‘core zone’ was legally given by DENR and further endorsed through a SEP clearance by the PCSD. This assertion gave more ground to Congressman Alvarez to challenge Romeo Dorado, PCSD executive director: “a permit to explore core zones is not just a piece of paper, it actually entails the manipulation and disturbance of areas that, in principle, should be maintained free of human disruption. If the PCSD has allowed the exploration of core zones, it means that there is something wrong here” said Alvarez. Director Romeo Dorado clarified that, although the area used by MAC for exploration purposes is mostly located in core zones, the PCSD is only prepared to endorse to MacroAsia 91ha area out of the total MAC MPSA area of about 1300ha. Dorado’s reassurance was unconvincing and raised more questions than answers. In fact, according to the evidence presented by ALDAW team, there are no signs of exploration in the proposed 91hectares, no test pits and drilling holes and – in fact – as it was later confirmed by MacroAsia itself - no valuable minerals are found in the applied area. “What’s the purpose of getting an endorsement for this area, while the minerals that the companies want to extract are located much further in the uplands?” asked Alvarez. Atty Gerthie Mayo-Anda picked up on this argument: “we should really understand the ‘economic implications’ of the 91-hectare area. Surely if the company does not consider it commercially viable to just mine 91 hectares, they would want a much larger area which means that their targets for mineral extraction are really the core zones and the protected area!” said Mayo-Anda. Again, MacroAsia representatives had no valid argument on which to cling and rather admitted that the 91ha area for which SEP clearance is requested will be used as an ‘installation base for the company’. Having said this, MAC representatives provided no information on the exact location where the actual mining extraction would actually take place. During the meeting, Atty. Mayo-Anda further stressed that MAC’s MPSA area is located inside the recently declared Mount Mantalingahan Protected Landscape (MMPL), pursuant to Presidential Proclamation no. 1815. MacroaAsia representatives contested the assertion by claiming that, according to the same Proclamation, any valid contract for the extraction of natural resources already existing prior to the proclamation should be respected until its expiration. According to Dr. Dario Novellino (CBCD researcher and partner of ALDAW) the MAC spokesmen omitted a very important paragraph found in the same proclamation which specifies that areas covered by such contracts, which are found not viable for development after assessment shall automatically form part of the MMPL. “According to our field research, the areas claimed by MAC is not viable for any form of aggressive development, due to its particular ecological characteristics and specific landscape value” said Novellino. Atty. Mayo-Anda further challenged the MAC spokesman by clarifying that “the vested argument is skewed and cannot be sustained. It is well-settled in Philippine jurisprudence that exploration, development and utilization of natural resources through licenses, concessions or leases are mere grants or privileges by the State; and being so, they may be revoked, rescinded, altered or modified when public interest so requires” said Mayo-Anda. While MacroAsia representatives admitted that their concession overlaps with the Mantalinghan Proclaimed area, they also questioned how much of it is really located in core zones. “Part of their defence argument was based on their own subjective interpretation of core zone. They kept arguing that ‘core zones’ are above 1000 m ASL, to prove that most of their exploration and extractive activities are legal, being below that altitude. In reality according to SEP law core zones do not just include areas above 1000 meters elevation but all types of natural forest: first growth forest, residual forest and edges of intact forest, endangered habitats, etc. These are exactly the kind of places where MAC has been concentrating its own mining activities” said Novellino.
To the surprise of both NGOs and indigenous participants, the representative of the Mineral Geoscience Bureau of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources proposed that it would be better to revise the ‘core zones’ rather than challenging the company’s actions and operations. Again this statement ignited the debate even further “ECAN amendment in Brooke’s Point would be inconsistent. Any proposed change to the zoning system should be discussed publically in a Barangay Assembly and in close consultation with the communities. Core zones should be protected rather than amended to accommodate the interests on the mining companies” responded Mayo-Anda and Congressman Alvarez.
In addition to geotagging and ocular inspection, MacroAsia was also challenged on the bases of social acceptability. “It will not be difficult to establish that the people of Brookes Point are overwhelmingly against any mining. This is what we indigenous peoples and farmers have been trying to communicate to the government for the past two years through public demonstrations and rallies but they did not listen” said ALDAW Chairman Artiso Mandawa.
MAC representatives insisted that, as far as social acceptability is concerned, all documentation from the National Council for Indigenous Peoples (NCIP) had already been secured. However, according to Commissioner Atty. Felongco representing the NCIP on the meeting “applications are still pending and no final decision by NCIP has been made. On the contrary, we have been requesting additional documentation to the local government, since two barangays have not yet been consulted”. Governor Baham, chairing the meeting, expressed his discontentment for the NCIP inability to respond promptly to the lack of documentation relating to ‘social acceptability’. “From now on, NCIP provincial office should communicate its findings directly to the NCIP national office. Passing through the regional office, delays the whole procedures and creates anomalies” said Governor B. Mitra. He also posed the question on whether and to what extent previous local government endorsements to MacroAsia would still be confirmed after the forthcoming Barangay election. “I think all these crucial matters should be re-discussed and reviewed by the new barangay administration, as soon as it is elected and become operative” said Governor Mitra. Adding more points to the argument, Atty. Mayo-Anda suggested “municipal government officials should visit personally the area claimed by MAC to get a clear idea of the location, vegetation cover and actual land uses; and such crucial decision cannot be made just by tracing lines on a map”. During the PCSD meeting, also former Congressman Alfredo Amor Abueg Jr. asked the Council for a re-evaluation of all requirements provided by MacroAsia, especially those related to Barangay government, NCIP and to the Province itself. “All previous endorsements given by the local government should now be re-evaluated on the bases of evidences brought forward by the ALDAW team” he said.
Hon. Baham Mitra, Governor of Palawan and newly elected PCSD chairman, finally approved the motion. This entails that the decision to endorse a SEP clearance to MacroAsia is deferred until a multipartite team composed of PCSD technical staff, local government officials, NGOs and Indigenous Peoples’ representatives visits the proposed area and investigates the ALDAW findings and all pending issues raised by the NGO community. The team should also be in charge of determining: 1) the legality of endorsements by local government units; 2) the expected impact of mining on indigenous culture and livelihood; 3) the potential impact of mining on tourism industry; 4) the economic value of the 91 hectares for which SEP clearance is being sought by MacroAsia.
“This is just an initial victory for the indigenous peoples and our NGOs supporters” commented Artiso Mandawa (ALDAW Chairman) at the end of the meeting. “It proves that illicit affairs are not unstoppable, when the evidence brought forward is there to light up every dark corner and to expose all bed practices of mining companies and their political allies” addend Mandawa.
Some reflections on the way forward
The last PSCD meeting agenda has shed light on a number of issues that apply not only to MacroaAsia but to the vast majority of mining companies in Palawan whose operations can be questioned both from the perspective of ‘social acceptability’ and ‘environmental sustainability’. Several major mining projects that are in the pipeline in Palawan have been endorsed by local government officials, but have not been approved by the communties that would host them. Mining incursion in core zones and forested areas of high-biological diversity has already occurred in other areas. Geotagging findings, as those collected with reference to MacroAsia MPSA area, have already been gathered for the concession areas of Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC) bordering MAC concession, as well as for Bulanjao range, one of the most valuable biodiversity hot spots in Southern Palawan. Here the mining road of Rio-Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation has already reached the highest fringes of the Bulanjao, at an latitude of 859m, causing deforestation, sever soil erosion and damage to the Sumbiling river watersheds. Evidence indicates that also the mining applications of Narra Nickel Mining and Development, Inc. (NNMDC), Tesoro Mining and Development, Inc. (TMDI), and McArthur Mining, Inc. (MMI) - approved through a Financial and Technical Assistance Agreement (FTAA) – and partnering with the Canadian MBMI - will surely encroach into core zones leading to the devastation of precious watersheds, indigenous ancestral territories and productive rice-land. The same applies to the City Nickel company in Espanola municipality and Fujian-Sino Mining Corp in Roax Municipality.
To avoid the transformation of Palawan (the Last Philippine’s Frontier) into a mining destination the following actions would be required.
The Local Government (LGU)
The LGU should ensure that all mining related decisions which are likely to affect local communities and their environment, be discussed with an independent committee formed by indigenous peoples, local farmers, NGOs and IPs organizations’ representatives in order to enhance transparency and accountability in decision making process.
Moreover, the LGUs should stick to their original Municipal Comprehensive Land Use Plans (CLUPs) without trying to reclassify ECAN zones into multiple/manipulative use zones to allow extractive activities.
The PCSD should stop issuing permits to mining companies to operate in ecologically precious and/or fragile areas, since this is in violation with the agency’s own mandate. Even more importantly, PCSD should stop any attempt of changing the definition of core zones and other zones to allow mining activities in forested land. It has already been established that some definitions such as those of ‘controlled use zones’ have been amended by the Council to please big corporations’ interests. For instance, according to the SEP law, in Controlled Use Area – (the outer protective barrier that encircles the core and restricted use areas) “strictly controlled mining and logging, which is not for profit…may be allowed”. Recently the ‘not for profit’ specification has been eliminated, thus opening these zones to commercial extractive activities.
Evidence, also indicate that PCSD maps are also inconsistent with the SEP zoning criteria. For instance, those areas that encircle and provide a protective buffer to the ‘core zones’, rather than being demarcated in blue (the color of restricted-use zones) are demarcated in brown, the color of ‘controlled use zones’ where mining is now allowed. These inconsistencies should be explained and rectified by the PCSD, as soon as possible.
Before, issuing SEP clearances the PCSD should consult indigenous and farmers communities. As of now, this has never been the case.
The Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR)
The DENR should stop fast-tracking mining contracts in Palawan. It should make watersheds off-limits to mining, as well as those areas of high biodiversity and endemism, to include Indigenous Peoples’ Ancestral Domains. This should lead to the suspension of all existing MPSA and FTAA until all controversial issues and ambiguities are clarified.
Ultimately, the DENR should solve its inherent conflict of interest caused by its dual functions: on one hand protecting the environment and the indigenous peoples and, on the other, promoting mining. Therefore, it is suggested that the responsibility related to the issuing of mining licenses should be dealt with by the Department of Mines, Hydrocarbons and Geosciences.
The NCIP
NCIP should stop issuing certificate of pre condition/clearances to mining applications and influencing indigenous peoples into endorsing mining projects. NCIP should also ensure that all FPIC processes carried out in conjunction with mining issues are evaluated by an independent body formed by indigenous leaders elected by their own communities, by representatives of indigenous organizations and, if the latter require so, by members (researchers, journalists, advocates, etc) of foreign institutions.
The National Government
The State should call for an immediate halt of mining operations in Palawan since such activities contravene those provisions contained in well-know conventions ratified by the Philippine Gove[e.g. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)], the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples. The Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage and; the Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage.
Ultimately, the National Government should revoke the 1995 mining act and issue a new act placing more emphasis on human rights and ecological balance, while regulating mining for the public interest.
The Provincial Government
In late 2008, the provincial board of Palawan has passed a provincial resolution providing for a moratorium on small-scale mining for a period of 25 years. This local legislative effort is not enough to prevent large scale and exploration activities in the province. The Provincial Government should prove and demonstrate to the National Government that the revitalization of the mining industry is not compatible with the special environmental status of Palawan Island, nor with the PCSD’s primary goal of achieving sustainable development in accordance with the Strategic Environmental Plan (RA 7611).
The UNESCO
Having established Palawan as a “Man and Biosphere Reserve” the UNESCO should play a more incisive and pro-active role, specifically when national governments, such as the Philippines, violate the condition for which such ‘prestigious awards’ have been granted.
Source: ALDAW
Friday, July 30, 2010
Participatory 3D Modelling used for the development of a community conserved area management plan in Mexico
 |
| Maps like this one will help the communties to have a better understanding of resources when developing their management plans; Photo: Irma Juan Carlos |
Oaxaca, Mexico: From March until May 2010, three university students from Chile and Mexico supported the ongoing work of Chinantec research teams to develop a management plan for their community conserved areas.
Andrés Basante, a master's student from the Environmental Geography Research Center of the National Autonomous University of Mexico (CIGA - UNAM), led a series of community mapping workshops.
Tomás Ibarra, a master's student at the University of Kent, conducted fieldwork for his dissertation on the influence of a hunting moratorium on socio-cultural change in the Chinantla.
Antonia Barreau worked as a research collaborator to conduct a short study entitled “Effects of conservation activities on diet patterns in Chinantec communities”.
These results will be returned to the communities to be integrated into their management programs.
Mesoamerica Coordinator
Source: Global Diversity Foundation Update; Issue 4, July 2010
Labels:
community mapping,
maqueta,
Mexico,
p3dm,
Participatory GIS,
pgis,
ppgis,
UNAM
Thursday, July 29, 2010
Recreando nuestra Cultura, Mapeando nuestro Futuro
El cuento de un encuentro especial en Venda, Sur Africa, y un proceso comunitario de cartografía eco-cultural. Líderes indígenas del Altai (Rusia) y la Amazonía Colombiana, juntos con representantes de ONGs de Sur Africa, Kenia y Etiopía, acompañan a la comunidad de Tshidvizhe mientras que descubren una sencilla pero poderosa manera de expresar el pasado y el presente de su territorio en mapas hechos a mano. Los mapas destacan la importancia de su cultura, los sitios sagrados, el territorio y sus modos de vida, y empoderan a la comunidad mapear el futuro por lo cual deben luchar.
Tuesday, July 27, 2010
Palawan ‘UNESCO Man and Biosphere Reserve’ in the grip of Mining Companies?
Puerto Princesa - ALDAW. On the 7th of June (see IC release) 600 protesters from farmers and indigenous communities reached the capital city of Puerto Princesa on Palawan Island requesting the Provincial Government not to endorse the proposed mining plans of MacroAsia and Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC). As a result of the negotiations taking place between the protesters’ delegation and policy makers in Puerto Princesa, the Provincial Government agreed that endorsement of both MacroAsia and INC should have required further investigation. However, that promise was not honoured and, after a few days, the Provincial Government gave his endorsement to MAC and INC to operate in one of the best conserved biocultural paradises found in the Philippines, and in South-East Asia as a whole.
The area given out to mining concession is also inhabited by traditional indigenous Palawan having limited contacts with the outside world. Moreover, the Gantong range and neighboring areas where MAC and INC intend to operate are within the area recently declared as Mount Mantalingahan Protected Landscape, pursuant to Presidential Proclamation no. 1815.
Both the MPSA areas of MacroAsia and INC are located in ecologically valuable areas which include watersheds, hunting/ agricultural grounds, extractive reserves of Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs) such as Almaciga (Agathis philippinensis) resin, on which upland indigenous communities depend for their daily subsistence. Also indigenous peoples’ sacred and worship sites are found within the mining tenements of these companies.
Representatives of ELAC (Environmental Legal Assistance Center) are now filing cases against government officials and their respective agencies for having endorsed MAC and INC without securing first the needed social acceptability requirements and in disregard of the Strategic Environmental Plan (Republic Act 7611).
Say ELAC Atty. Edward G. Lorenzo: “the sustainable management of the entire Province is, in fact, governed by the SEP law which prohibits any human activity in those areas that are classified as ‘core zones’ and that – very unfortunately - are now part of MAC and INC mining tenements”. A indigenous member of the indigenous community of Gieb (Barangay Maasin, Brooke’s Point Municipality) also claims: “they (mining personnel of MAC) just entered our land without asking permission, and they removed our rice plants to excavate big ditches in our agricultural fields and also up into the mountains, only few meters away from the Balgtik (Agathis Philippinensis) trees that we sell and from which we depend for our survival”. According to another member of the same community: “MacroAsia peoples have removed soil and trees also in those sacred forest that we call lylien and that are inhabited by powerful super-human beings (Taw Kawasa)”.
Between 12-16 July a geotagging field reconnaissance carried out by the ALDAW (Ancestral/Land Domain Watch) in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent has confirmed that MacroAsia test pits and drilling holes are found in ‘core zones’ (areas of maximum protection) around and even above 1,000 m ASL. Indigenous peoples trained on basic GPS and Geotagging technologies, with their own set of equipment divided into two groups to cover a large portion of the MAC and INC mining tenement area.
It appears that both MAC and INC have violated the basic tenets of the Strategic Environmental Plan (SEC) and also of the Indigenous Peoples Rights Act (IPRA Law), a national law protecting the interests of Indigenous Cultural Communities (ICC). Faced by this and similar accusations, the Provincial Government recently made a statement according to which MacroAsia and INC may not be allowed to operate in core zones, but their activities might be limited only to multiple/manipulative use areas. Again, ocular inspection and GPS data obtained by ALDAW and CBCD indicate the those portions of MacroAsia and INC mining concessions, which are outside the core zones, still include forested buffer zones which, obviously, do not fit by any means into the standard definition of ‘multiple/manipulative use zones’, where – according to the law – mining might be allowed. In fact, the mining claims of both MAC and INC are entirely located in ‘core zones’, ‘restricted zones’, agricultural and agroforestry areas that are subject to various cropping regimes. All these categories, according to the SEP law, should not be subject to any other form of large-scale extractive activity.
Also, lowland farmers are extremely concerned about the siltation of their wet-rice cultivation, as all irrigation water coming into their fields originates from the mountains where mining is supposed to take place. Members of academic institutions have suggested that: unless these precious water catchments are protected from mining operations, at least 50% of Brooke’s point sustainable agriculture, which requires irrigation, might be lost.
Says a spokesman of Alyansa Tigil Mina (the largest anti-mining advocacy group in the country) “Ironically enough the mining companies and the politicians who are endorsing them have also infringed the Philippine Mining Act which prohibits mining in old growth or virgin forest, proclaimed watershed forest reserves, wilderness area, and other areas of outstanding environmental value”. According to Atty. Mary Jean Feliciano of the ALDAW Network “in endorsing the mining exploration of both MAC and INC, the Sangguniang Bayan (Local Government of Brooke’s Point) has acted in contradiction with its own Municipal Comprehensive Land Use Plan (CLUP) for 2000-2010, in which mining was never considered as a development strategy and, in doing so, it has also bypassed the interests of local communities, as well as all forms of public consultations”.
Undoubtedly, the endorsement by both Local and Provincial governments of the proposed operations of MAC and INC contravenes also those provisions contained in well know conventions [e.g. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples that the Philippine Government has already signed. Says a member of the Palawan advocacy community: “When the Government itself infringes its own laws so bluntly, it means that the fundamentals of democracy are breaking apart and a new form of state-led terrorism is coming into being to deprive hundreds of farmers and indigenous peoples of their traditional, and thus legitimate sources of life, just to benefit a handful of greedy and irresponsible businessmen and their cronies”.
On July 30, 2010 the members of the Palawan Council for Sustainable Development (PCSD) - a local government body in charge of the protection and sustainable management of the province - will meet to decide whether to issue a SEP clearance to the operations of MacroAsia and Ipilan Nickel Corporations. The future of one of the most pristine forests in the Philippines and the life of thousands of peoples who depend from it, is now in the hands of the Council.
Indigenous peoples and their networks, farmers, fisher folks, the Palawan NGO Network Inc (PNNI) and its associates, are uniting their effort to convince the PCSD to take a responsible decision which will ensure the sustainable future of Brook’s Point Municipality and of its biocultural diversity.
What you can do ...
Sign a Petition to Stop Mining in Palawan!
And address your concerns to:
Palawan Council for Sustainable Development
oed@pcsd.ph . and c/o Mearl Hilario mearlhilario@yahoo.com
FAX: 0063 (048) 434-4234
Honorable Governor of Palawan
Baham Mitra
abmitra2001@yahoo.com
FAX: 0063 (048) 433-2948
For more information watch ALDAW videos
http://www.vimeo.com/aldawnetwork
http://www.youtube.com/user/ALDAWpalawan
http://hub.witness.org/en/users/aldaw-network
or contact the ALDAW Network (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) aldawnetwork@gmail.com and Alyansa Tigil Mina (nc@alyansatigilmina.net / alyansatigilmina@gmail.com )
The area given out to mining concession is also inhabited by traditional indigenous Palawan having limited contacts with the outside world. Moreover, the Gantong range and neighboring areas where MAC and INC intend to operate are within the area recently declared as Mount Mantalingahan Protected Landscape, pursuant to Presidential Proclamation no. 1815.
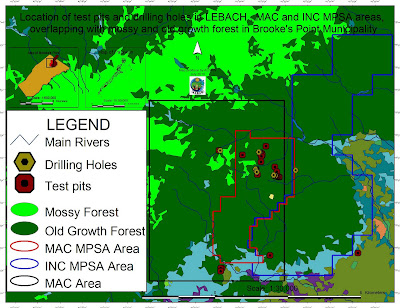 |
| Location of test pits and drilling holes within the mining concessions and their overlap with mossy and old growth forest in Brook's Point Municipality |
Representatives of ELAC (Environmental Legal Assistance Center) are now filing cases against government officials and their respective agencies for having endorsed MAC and INC without securing first the needed social acceptability requirements and in disregard of the Strategic Environmental Plan (Republic Act 7611).
Say ELAC Atty. Edward G. Lorenzo: “the sustainable management of the entire Province is, in fact, governed by the SEP law which prohibits any human activity in those areas that are classified as ‘core zones’ and that – very unfortunately - are now part of MAC and INC mining tenements”. A indigenous member of the indigenous community of Gieb (Barangay Maasin, Brooke’s Point Municipality) also claims: “they (mining personnel of MAC) just entered our land without asking permission, and they removed our rice plants to excavate big ditches in our agricultural fields and also up into the mountains, only few meters away from the Balgtik (Agathis Philippinensis) trees that we sell and from which we depend for our survival”. According to another member of the same community: “MacroAsia peoples have removed soil and trees also in those sacred forest that we call lylien and that are inhabited by powerful super-human beings (Taw Kawasa)”.
Between 12-16 July a geotagging field reconnaissance carried out by the ALDAW (Ancestral/Land Domain Watch) in collaboration with the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) of the University of Kent has confirmed that MacroAsia test pits and drilling holes are found in ‘core zones’ (areas of maximum protection) around and even above 1,000 m ASL. Indigenous peoples trained on basic GPS and Geotagging technologies, with their own set of equipment divided into two groups to cover a large portion of the MAC and INC mining tenement area.
It appears that both MAC and INC have violated the basic tenets of the Strategic Environmental Plan (SEC) and also of the Indigenous Peoples Rights Act (IPRA Law), a national law protecting the interests of Indigenous Cultural Communities (ICC). Faced by this and similar accusations, the Provincial Government recently made a statement according to which MacroAsia and INC may not be allowed to operate in core zones, but their activities might be limited only to multiple/manipulative use areas. Again, ocular inspection and GPS data obtained by ALDAW and CBCD indicate the those portions of MacroAsia and INC mining concessions, which are outside the core zones, still include forested buffer zones which, obviously, do not fit by any means into the standard definition of ‘multiple/manipulative use zones’, where – according to the law – mining might be allowed. In fact, the mining claims of both MAC and INC are entirely located in ‘core zones’, ‘restricted zones’, agricultural and agroforestry areas that are subject to various cropping regimes. All these categories, according to the SEP law, should not be subject to any other form of large-scale extractive activity.
Also, lowland farmers are extremely concerned about the siltation of their wet-rice cultivation, as all irrigation water coming into their fields originates from the mountains where mining is supposed to take place. Members of academic institutions have suggested that: unless these precious water catchments are protected from mining operations, at least 50% of Brooke’s point sustainable agriculture, which requires irrigation, might be lost.
Says a spokesman of Alyansa Tigil Mina (the largest anti-mining advocacy group in the country) “Ironically enough the mining companies and the politicians who are endorsing them have also infringed the Philippine Mining Act which prohibits mining in old growth or virgin forest, proclaimed watershed forest reserves, wilderness area, and other areas of outstanding environmental value”. According to Atty. Mary Jean Feliciano of the ALDAW Network “in endorsing the mining exploration of both MAC and INC, the Sangguniang Bayan (Local Government of Brooke’s Point) has acted in contradiction with its own Municipal Comprehensive Land Use Plan (CLUP) for 2000-2010, in which mining was never considered as a development strategy and, in doing so, it has also bypassed the interests of local communities, as well as all forms of public consultations”.
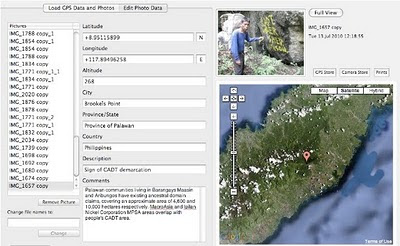 |
| Cornerstone of a CADT (Certificate of Ancestral Domain Title) |
Undoubtedly, the endorsement by both Local and Provincial governments of the proposed operations of MAC and INC contravenes also those provisions contained in well know conventions [e.g. The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples that the Philippine Government has already signed. Says a member of the Palawan advocacy community: “When the Government itself infringes its own laws so bluntly, it means that the fundamentals of democracy are breaking apart and a new form of state-led terrorism is coming into being to deprive hundreds of farmers and indigenous peoples of their traditional, and thus legitimate sources of life, just to benefit a handful of greedy and irresponsible businessmen and their cronies”.
On July 30, 2010 the members of the Palawan Council for Sustainable Development (PCSD) - a local government body in charge of the protection and sustainable management of the province - will meet to decide whether to issue a SEP clearance to the operations of MacroAsia and Ipilan Nickel Corporations. The future of one of the most pristine forests in the Philippines and the life of thousands of peoples who depend from it, is now in the hands of the Council.
Indigenous peoples and their networks, farmers, fisher folks, the Palawan NGO Network Inc (PNNI) and its associates, are uniting their effort to convince the PCSD to take a responsible decision which will ensure the sustainable future of Brook’s Point Municipality and of its biocultural diversity.
What you can do ...
Sign a Petition to Stop Mining in Palawan!
And address your concerns to:
Palawan Council for Sustainable Development
oed@pcsd.ph . and c/o Mearl Hilario mearlhilario@yahoo.com
FAX: 0063 (048) 434-4234
Honorable Governor of Palawan
Baham Mitra
abmitra2001@yahoo.com
FAX: 0063 (048) 433-2948
For more information watch ALDAW videos
http://www.vimeo.com/aldawnetwork
http://www.youtube.com/user/ALDAWpalawan
http://hub.witness.org/en/users/aldaw-network
or contact the ALDAW Network (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) aldawnetwork@gmail.com and Alyansa Tigil Mina (nc@alyansatigilmina.net / alyansatigilmina@gmail.com )
Friday, July 23, 2010
Le projet de cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo
Freddy Nguema Allogo est responsable technique du projet cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo par compte de Brainforest Gabon. Freddy décrives le projet et son état d’avancement.
Le projet régional de cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo pour la République du Congo a été lancé le 18 juin à Brazzaville. Initié par la Rainforest Foundation du Royaume Uni, ce projet qui s’étalera sur deux ans, sera mis en œuvre par l’Observatoire congolais des droits de l’homme (OCDH).
L’objectif global de la cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo est de promouvoir l’inclusion des droits des communautés forestières pour un contrôle et une utilisation rationnelle des forêts.
Le projet vise à renforcer les capacités des communautés forestières, de l’administration et des organisations de la société civile à mieux connaître les ressources forestières ; à soutenir les communautés forestières dans leur dialogue avec les autorités compétentes.
L’initiative de Rainforest Foundation traduit la volonté du Gouvernement anglais de ralentir le processus de déforestation par le développement des capacités des populations et des institutions des pays du Bassin du Congo dans la gestion durable des forêts, tout en assurant les meilleures conditions de vie aux communautés locales.
Ainsi, ces cartes géo référencées, une fois produites, devront mettre en valeur la richesse des écosystèmes forestiers du Congo et souligner les dimensions économiques, sociales et culturelles qu’ils représentent pour les populations qui y vivent
Le projet régional de cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo pour la République du Congo a été lancé le 18 juin à Brazzaville. Initié par la Rainforest Foundation du Royaume Uni, ce projet qui s’étalera sur deux ans, sera mis en œuvre par l’Observatoire congolais des droits de l’homme (OCDH).
L’objectif global de la cartographie participative dans le Bassin du Congo est de promouvoir l’inclusion des droits des communautés forestières pour un contrôle et une utilisation rationnelle des forêts.
Le projet vise à renforcer les capacités des communautés forestières, de l’administration et des organisations de la société civile à mieux connaître les ressources forestières ; à soutenir les communautés forestières dans leur dialogue avec les autorités compétentes.
L’initiative de Rainforest Foundation traduit la volonté du Gouvernement anglais de ralentir le processus de déforestation par le développement des capacités des populations et des institutions des pays du Bassin du Congo dans la gestion durable des forêts, tout en assurant les meilleures conditions de vie aux communautés locales.
Ainsi, ces cartes géo référencées, une fois produites, devront mettre en valeur la richesse des écosystèmes forestiers du Congo et souligner les dimensions économiques, sociales et culturelles qu’ils représentent pour les populations qui y vivent
Tuesday, July 06, 2010
High resolution participatory satellite imagery interpretation in Southern Etiopia
A SPOT 5 scene was used to explore indigenous land use patterns, pastoral rangeland management and infrastructures with Borana pastoralist, a customary institution in Oromia region, Southern Ethiopia. Video material produced in August 2009. Contribution: Massimiliano Rossi
Sunday, June 13, 2010
RROMUEPATSRO: Mapping the Historical-Cultural Space of the Yanesha, Perú
This video is the first in a series titled “Where Our Ancestors Walked: Mapping the Historical-Cultural Space of the Yanesha People,” which was made in collaboration with the Yanesha people in order to preserve their history and its relation with their territory as sacred landscape. Rromuepatsro presents the Yanesha people, located in the eastern slope of the Peruvian central Andes, and explores their vital relationship with their ancestors and the natural landscape. It shows how they have used PGIS, anthropological research and Yanesha oral history to map their historical cultural space and thus reaffirm their millennial link to the ancient world and the civilization of the central Andes.
This video has been produced in Spanish and English by the Instituto del Bien Común (IBC), Lima, Perú.
Wednesday, June 09, 2010
Reviving our culture, Mapping our future
The story of a special gathering in Venda, South Africa, and a community process in eco-cultural mapping. Indigenous leaders from Altai (Russia) and the Colombian Amazon, and NGO representatives from South Africa, Kenya and Ethiopia, accompany Tshidvizhe community as they explore a simple yet powerful way to express the past and present of their territory and livelihoods onto hand-drawn maps. The maps highlight the importance of their culture, sacred sites and territory, and empower them to map the future they need to strive for.
Production: The Gaia Foundation, African Biodiversity Network (ABN), Mupo Foundation and the Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Co-operation ACP-EU (CTA).
Friday, June 04, 2010
Participatory mapping at IFAD
The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) is implementing the project “Piloting IFAD’s Participatory Mapping Approach for Specific Livelihoods” through innovative twinning arrangements.
The second phase of the project has focused on participatory mapping. As a result IFAD published “Good Practices in Participatory Mapping” and the “IFAD Adaptive Approach to Participatory Mapping”.
The next phase is focusing is participatory monitoring and evaluation of participatory mapping processes.
Below are the main outcomes of the second phase:
The second phase of the project has focused on participatory mapping. As a result IFAD published “Good Practices in Participatory Mapping” and the “IFAD Adaptive Approach to Participatory Mapping”.
The next phase is focusing is participatory monitoring and evaluation of participatory mapping processes.
Below are the main outcomes of the second phase:
- The International Fund for Agricultural Development (Corbett J. M.) (2009) “ Good practices in participatory mapping.” The International Fund for Agricultural Development, Rome, Italy. 55 pages.
- Le Fonds international de développement agricole (Corbett J. M.) 2009. Cartographie participative et bonnes pratiques. Le Fonds international de développement agricole (FIDA), Rome, Italie. 59 pages
- El Fondo Internacional de Desarrollo Agrícola (Corbett J.M) 2009. Buenas prácticas en cartografía participativa. Análisis preparado para el Fondo Internacional de Desarrollo Agrícola (FIDA). Roma, Italia. 59 paginas
- The International Fund for Agricultural Development (Corbett J. M.) (2010) “Adaptive Mapping: IFAD Design and Delivery of Participatory Mapping Projects.” The International Fund for Agricultural Development, Rome, Italy. pp. 47
Tuesday, June 01, 2010
Whose Map? | ¿De Quién Son Los Mapas? | à qui appartiennent les cartes ? English / français/ español
In recent years, changes in participatory methodologies (PMs) may have been even more rapid than those in spatial technologies. Local people's abilities to make maps only became widely known and facilitated in the early 1990s. In this article Dr. Robert Chambers argues that participatory mapping has spread like a pandemic with many variants and applications not only in natural resource management but also in many other domains. With mapping as one element, there are now signs of a new pluralist eclecticism and creativity in PMs. The medium and means of mapping, whether ground, paper or GIS and the style and mode of facilitation, influence who takes part, the nature of outcomes and power relationships. Much depends on the behaviour and attitudes of facilitators and who controls the process. Many ethical issues present troubling dilemmas, and lead to overarching questions about empowerment and ownership. Questions to be asked, again and again, are: Who is empowered and who disempowered? And, who gains and who loses?
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
- Robert Chambers. 2006. Participatory Mapping and Geographic Information Systems: Whose Map? Who is Empowered and Who Disempowered? Who Gains and Who Loses? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-11
- Robert Chambers. 2006. El Mapeo Participativo Y Los Sistemas De Información Geográfica: ¿De Quién Son Los Mapas? ¿Quién Se Empodera Y Quién Se Desempodera? ¿Quién Gana Y Quién Pierde? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-14 - Traducido y publicado por: Centro Técnico para la Cooperación Agricultural y Rural ACP-EU (CTA), 2010. Con la autorización de: EJISDC
- Robert Chambers. 2006. Cartographie participative et systèmes d’information géographique : à qui appartiennent les cartes ? Qui en ressort renforcé, qui en ressort affaibli ? Qui gagne et qui perd ? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-14 - Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission d’EJISDC
Sunday, May 30, 2010
Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication in Developing Countries / English / Français / Español
The merging of participatory development methods with geo-spatial technologies has come to be known as Participatory GIS and is now an emergent development practice in its own right. PGIS combines a range of geo-spatial information management tools and methods such as sketch maps, participatory 3D models, community-based air photo and satellite imagery interpretation, GPS transect walks and GIS-based cognitive mapping. Participatory GIS implies making GIT&S available to disadvantaged groups in society in order to enhance their capacity in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information.
PGIS practice is geared towards community empowerment through measured, demand-driven, user-friendly and integrated applications of geo-spatial technologies. GIS-based maps and spatial analysis thus become major conduits in the process. A good PGIS practice is embedded into long-lasting and locally driven spatial decision-making processes, is flexible, adapts to different socio-cultural and bio-physical environments, depends on multidisciplinary facilitation and skills and builds essentially on visual language. If appropriately utilized, the practice should exert profound impacts on community empowerment, innovation and social change. More importantly, by placing control of access and use of culturally sensitive spatial information in the hands of those who generated them, PGIS practice can protect traditional knowledge and wisdom from external exploitation.
Effective participation is the key to good PGIS practice. Whilst the focus of traditional GIS applications is often on the outcome, PGIS initiatives tend to emphasize the processes by which outcomes are attained. At times the participatory process can obfuscate systematic inequalities through unequal and superficial participation. For example, PGIS applications may be used to legitimise decisions which in fact were taken by outsiders. The process can also easily be hijacked by community elites. For PGIS practices to be successful, they must be placed in a well thought out and demand-driven process based on the proactive collaboration of the custodians of local and traditional knowledge and of facilitators skilled in applying PGIS and transferring technical know-how to local actors. Participation thus cuts across the process from gaining a clear understanding of the existing legal and regulatory frameworks, to jointly setting project objectives, defining strategies and choosing appropriate geo-spatial information management tools. The integrated and multifaceted nature of PGIS provides legitimacy for local knowledge and generates a great sense of confidence and pride which prepares participant communities in dealing with outsiders. The process is intended to build self-esteem, raise awareness about pressing issues in the community and produce concrete and sustainable spatial solutions.
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
Selected publications on the subject are available at www.gis4d.com
PGIS practice is geared towards community empowerment through measured, demand-driven, user-friendly and integrated applications of geo-spatial technologies. GIS-based maps and spatial analysis thus become major conduits in the process. A good PGIS practice is embedded into long-lasting and locally driven spatial decision-making processes, is flexible, adapts to different socio-cultural and bio-physical environments, depends on multidisciplinary facilitation and skills and builds essentially on visual language. If appropriately utilized, the practice should exert profound impacts on community empowerment, innovation and social change. More importantly, by placing control of access and use of culturally sensitive spatial information in the hands of those who generated them, PGIS practice can protect traditional knowledge and wisdom from external exploitation.
Effective participation is the key to good PGIS practice. Whilst the focus of traditional GIS applications is often on the outcome, PGIS initiatives tend to emphasize the processes by which outcomes are attained. At times the participatory process can obfuscate systematic inequalities through unequal and superficial participation. For example, PGIS applications may be used to legitimise decisions which in fact were taken by outsiders. The process can also easily be hijacked by community elites. For PGIS practices to be successful, they must be placed in a well thought out and demand-driven process based on the proactive collaboration of the custodians of local and traditional knowledge and of facilitators skilled in applying PGIS and transferring technical know-how to local actors. Participation thus cuts across the process from gaining a clear understanding of the existing legal and regulatory frameworks, to jointly setting project objectives, defining strategies and choosing appropriate geo-spatial information management tools. The integrated and multifaceted nature of PGIS provides legitimacy for local knowledge and generates a great sense of confidence and pride which prepares participant communities in dealing with outsiders. The process is intended to build self-esteem, raise awareness about pressing issues in the community and produce concrete and sustainable spatial solutions.
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication in Developing Countries. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9 .
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Gestion Participative de l’information Géographique et de la Communication dans les Pays en Développement. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9. Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission d’EJISDC
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Manejo y Comunicación de la Información Territorial en Forma Participativa en los Países en vía de Desarrollo. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9. Traducido y publicado por: Centro Técnico para la Cooperación Agricultural y Rural ACP-EU (CTA), 2010. Con permiso de: EJISDC
Selected publications on the subject are available at www.gis4d.com
Thursday, May 27, 2010
PPgis.net Open Forum on Participatory Geographic Information Systems and Technologies

PPgis.net serves as a global avenue for discussing issues, sharing experiences and good practices related to community mapping, public participation GIS (PPGIS), participatory GIS (PGIS) and other geographic information technologies used to support integrated conservation and development, sustainable natural resource management and customary property rights in developing countries and among indigenous people worldwide.
Members of the network are able to share information and lessons learned, post questions and announcements and upload and download resource documents which are relevant to the practice.
The site is an online gateway for accessing discussion lists in English, French, Spanish and Portuguese, all dealing with participatory mapping.
Monday, May 24, 2010
Mapping Indigenous Lands / Mapeo de tierras indígenas / Cartographier les territoires autochtones
We have just completed the translation of this important publication by Mac Chapin & colleagues.
Here are the links to the documents.
Here are the links to the documents.
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapping Indigenous Lands. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapeo de tierras indígenas. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traducido y publicado por el Centro Técnico de Cooperación Agrícola y Rural (CTA), con autorización de ―Annual Review of Anthropology‖
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Cartographier les territoires autochtones. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission de « Annual Review of Anthropology »
Monday, May 17, 2010
Participatory Action Research Approaches and Methods: Connecting People, Participation and Place
Participatory Action Research (PAR) approaches and methods have seen an explosion of recent interest in the social and environmental sciences. PAR involves collaborative research, education and action which is oriented towards social change, representing a major epistemological challenge to mainstream research traditions. It has recently been the subject of heated critique and debate and rapid theoretical and methodological development.
This book captures these developments, exploring the justification, theorisation, practice and implications of PAR. It offers a critical introduction to understanding and working with PAR in different social, spatial and institutional contexts. The authors engage with PAR’s radical potential, while maintaining a critical awareness of its challenges and dangers. The book is divided into three parts. The first part explores the intellectual, ethical and pragmatic contexts of PAR; the development and diversity of approaches to PAR; recent poststructuralist perspectives on PAR as a form of power; the ethic of participation; and issues of safety and well-being. Part two is a critical exploration of the politics, places and practices of PAR. Contributors draw on diverse research experiences with differently situated groups and issues including environmentally sustainable practices, family livelihoods, sexual health, gendered experiences of employment, and specific communities such as people with disabilities, migrant groups, and young people. The principles, dilemmas and strategies associated with participatory approaches and methods including diagramming, cartographies, art, theatre, photovoice, video and geographical information systems are also discussed. Part three reflects on how effective PAR is, including the analysis of its products and processes, participatory learning, representation and dissemination, institutional benefits and challenges, and working between research, action, activism and change.
The authors find that a spatial perspective and an attention to scale offer helpful means of negotiating the potentials and paradoxes of PAR. This approach responds to critiques of PAR by highlighting how the spatial politics of practising participation can be mobilised to create more effective and just research processes and outcomes. The book adds significant weight to the recent critical reappraisal of PAR, suggesting why, when, where and how we might take forward PAR’s commitment to enabling collaborative social transformation. It will be particularly useful to researchers and students of Human Geography, Development Studies and Sociology.
This book captures these developments, exploring the justification, theorisation, practice and implications of PAR. It offers a critical introduction to understanding and working with PAR in different social, spatial and institutional contexts. The authors engage with PAR’s radical potential, while maintaining a critical awareness of its challenges and dangers. The book is divided into three parts. The first part explores the intellectual, ethical and pragmatic contexts of PAR; the development and diversity of approaches to PAR; recent poststructuralist perspectives on PAR as a form of power; the ethic of participation; and issues of safety and well-being. Part two is a critical exploration of the politics, places and practices of PAR. Contributors draw on diverse research experiences with differently situated groups and issues including environmentally sustainable practices, family livelihoods, sexual health, gendered experiences of employment, and specific communities such as people with disabilities, migrant groups, and young people. The principles, dilemmas and strategies associated with participatory approaches and methods including diagramming, cartographies, art, theatre, photovoice, video and geographical information systems are also discussed. Part three reflects on how effective PAR is, including the analysis of its products and processes, participatory learning, representation and dissemination, institutional benefits and challenges, and working between research, action, activism and change.
The authors find that a spatial perspective and an attention to scale offer helpful means of negotiating the potentials and paradoxes of PAR. This approach responds to critiques of PAR by highlighting how the spatial politics of practising participation can be mobilised to create more effective and just research processes and outcomes. The book adds significant weight to the recent critical reappraisal of PAR, suggesting why, when, where and how we might take forward PAR’s commitment to enabling collaborative social transformation. It will be particularly useful to researchers and students of Human Geography, Development Studies and Sociology.
Sunday, May 16, 2010
Choosing a participatory mapping method versus another
PGIS practitioners make use of a range of low and high tech geographic information technologies for acquisition, validation, analysis, representation and sharing of geo-spatial information. There are a number of factors that influence the choice of one method over another or the combination of more than one method. Factors include the ‘purpose behind the initiative’, the ‘resources available’ and the ‘institutional setting or environment’.
The choice of method should emanate predominantly from within the community . Participatory maps often represent a socially or culturally distinct understanding of land and seascapes and include information that is excluded from mainstream maps. These usually represent the views of the dominant sectors of society. Participatory maps can pose alternatives to the languages and images of the existing power structures and become a medium of empowerment by allowing local communities to represent themselves spatially.
For this reason, participatory maps should be made through an inclusive process at community level. The higher the level of participation by all members of the community, the more beneficial the outcome because the final maps, and related outputs like multimedia, will reflect the collective knowledge, concerns and aspirations.
In September 2010, CTA and IFAD will launch a Training Kit dedicated to “Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication” and having the specific objective of supporting the spread of good practice in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information. More information on the training kit will be made available on the Internet and on this blog.
The choice of method should emanate predominantly from within the community . Participatory maps often represent a socially or culturally distinct understanding of land and seascapes and include information that is excluded from mainstream maps. These usually represent the views of the dominant sectors of society. Participatory maps can pose alternatives to the languages and images of the existing power structures and become a medium of empowerment by allowing local communities to represent themselves spatially.
For this reason, participatory maps should be made through an inclusive process at community level. The higher the level of participation by all members of the community, the more beneficial the outcome because the final maps, and related outputs like multimedia, will reflect the collective knowledge, concerns and aspirations.
In September 2010, CTA and IFAD will launch a Training Kit dedicated to “Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication” and having the specific objective of supporting the spread of good practice in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information. More information on the training kit will be made available on the Internet and on this blog.
Wednesday, May 12, 2010
Participatory Video Validates Geo-Tagging Evidences on Mining Threats to Palawan Ecology and Indigenous Livelihoods
A field update from the ALDAW Network (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch)
May 2010
Between July and September 2009, a mission organized by the Philippines-based Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW) and the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) at the University of Kent demonstrated how the ecological balance and the survival of vulnerable indigenous communities on Palawan Island (a “Man and Biosphere Reserve” program of UNESCO) is being threatened by the ongoing mining rush. The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of mining firms, such as MacroAsia and Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporations, overlap with precious watersheds and the so called “core zones” of maximum protection. During the mission indigenous communities were engaged in the making and editing of participatory videos.
Today the voices of these isolated Palawan communities are available through the following links:
http://www.youtube.com/user/ALDAWpalawan
http://vimeo.com/aldawnetwork
May 2010
Between July and September 2009, a mission organized by the Philippines-based Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW) and the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) at the University of Kent demonstrated how the ecological balance and the survival of vulnerable indigenous communities on Palawan Island (a “Man and Biosphere Reserve” program of UNESCO) is being threatened by the ongoing mining rush. The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of mining firms, such as MacroAsia and Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporations, overlap with precious watersheds and the so called “core zones” of maximum protection. During the mission indigenous communities were engaged in the making and editing of participatory videos.
Today the voices of these isolated Palawan communities are available through the following links:
http://www.youtube.com/user/ALDAWpalawan
http://vimeo.com/aldawnetwork
Wednesday, April 28, 2010
ILO Convention on indigenous and tribal peoples: a manual
This is an easy-to-use manual to ILO Convention No. 169. It helps to understand the Convention, and how it can be used to gain recognition, promotion and protection of indigenous and tribal peoples' rights.
The manual - dated 2003 - does not explain each article of the Convention. It focuses on key concepts such as, for example, human rights, culture,land, development, education and health.
Nor does it strictly follow the structure of the Convention. It is divided into different sections. Each section deals with a key concept.
For easy reference, the manual has included the article or articles of the Convention which are being discussed. There is a descriptive explanation of each article. Concepts are introduced by using examples and experiences from indigenous and tribal peoples. This is to demonstrate the articles of the Convention in a practical way. ILO also included diagrams and photographs which highlight and explain some important elements of the articles.
The manual - dated 2003 - does not explain each article of the Convention. It focuses on key concepts such as, for example, human rights, culture,land, development, education and health.
Nor does it strictly follow the structure of the Convention. It is divided into different sections. Each section deals with a key concept.
For easy reference, the manual has included the article or articles of the Convention which are being discussed. There is a descriptive explanation of each article. Concepts are introduced by using examples and experiences from indigenous and tribal peoples. This is to demonstrate the articles of the Convention in a practical way. ILO also included diagrams and photographs which highlight and explain some important elements of the articles.
Wednesday, April 21, 2010
Rethinking the Power of Maps
 A contemporary follow-up to the bestselling Power of Maps, this book takes a fresh look at what maps do, whose interests they serve, and how they can be used in surprising, creative, and radical ways.
A contemporary follow-up to the bestselling Power of Maps, this book takes a fresh look at what maps do, whose interests they serve, and how they can be used in surprising, creative, and radical ways.In Rethinking the Power of Maps, Denis Wood describes how cartography facilitated the rise of the modern state and how maps continue to embody and project the interests of their creators. He demystifies the hidden assumptions of map making and explores the promises and limitations of diverse counter-mapping practices today.
Thought-provoking illustrations include U.S. Geological Survey maps; electoral and transportation maps; and numerous examples of critical cartography, participatory GIS, and map art.
Wednesday, March 24, 2010
Power of Maps: (Counter) Mapping for Conservation
This paper considers what is at stake in defining and mapping protected areas for conservation. The authors link issues of power in cartography to themes from political ecology, social natures, and conservation biology literatures to extend our understanding of maps as reflective of, and productive of, power. Reviewing insights from these literatures to consider power asymmetries common to conservation practice, they highlight ways that mapping practices and products reinforce and contribute to such dynamics.
The authors argue that in doing so enriches consideration of the power geometries of conservation cartographies by inviting fuller consideration of diverse species and landscapes, as well as enabling discussion of other representational and productive effects of conservation mappings. Once determined, how might conservation maps serve to naturalize certain spaces or boundaries as fixed, or contribute to certain socio-psychological understandings of conservation possibilities or outcomes?
In the closing sections, the authors invoke the idea of ‘counter-mapping’ to explore strategies that might redress these concerns. Possibilities range from efforts to adapt the form of protected areas to more critical approaches that question the appropriateness of territorial focus and mapping practices for conservation goals.
In conclusion, Harris and Hazen argue that theorizing power in human, other-than-human, and inter-species contexts is essential to understanding the power geometries of conservation mapping.
Citation: Leila M. Harris and Helen D. Hazen, 2006. Power of Maps: (Counter) Mapping for Conservation. ACME: An International E-Journal for Critical Geographies, 4 (1), 99-130
The authors argue that in doing so enriches consideration of the power geometries of conservation cartographies by inviting fuller consideration of diverse species and landscapes, as well as enabling discussion of other representational and productive effects of conservation mappings. Once determined, how might conservation maps serve to naturalize certain spaces or boundaries as fixed, or contribute to certain socio-psychological understandings of conservation possibilities or outcomes?
In the closing sections, the authors invoke the idea of ‘counter-mapping’ to explore strategies that might redress these concerns. Possibilities range from efforts to adapt the form of protected areas to more critical approaches that question the appropriateness of territorial focus and mapping practices for conservation goals.
In conclusion, Harris and Hazen argue that theorizing power in human, other-than-human, and inter-species contexts is essential to understanding the power geometries of conservation mapping.
Citation: Leila M. Harris and Helen D. Hazen, 2006. Power of Maps: (Counter) Mapping for Conservation. ACME: An International E-Journal for Critical Geographies, 4 (1), 99-130
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)








