Tuesday, July 06, 2010
High resolution participatory satellite imagery interpretation in Southern Etiopia
A SPOT 5 scene was used to explore indigenous land use patterns, pastoral rangeland management and infrastructures with Borana pastoralist, a customary institution in Oromia region, Southern Ethiopia. Video material produced in August 2009. Contribution: Massimiliano Rossi
Monday, May 24, 2010
Mapping Indigenous Lands / Mapeo de tierras indígenas / Cartographier les territoires autochtones
Here are the links to the documents.
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapping Indigenous Lands. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapeo de tierras indígenas. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traducido y publicado por el Centro Técnico de Cooperación Agrícola y Rural (CTA), con autorización de ―Annual Review of Anthropology‖
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Cartographier les territoires autochtones. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission de « Annual Review of Anthropology »
Monday, May 17, 2010
Participatory Action Research Approaches and Methods: Connecting People, Participation and Place
This book captures these developments, exploring the justification, theorisation, practice and implications of PAR. It offers a critical introduction to understanding and working with PAR in different social, spatial and institutional contexts. The authors engage with PAR’s radical potential, while maintaining a critical awareness of its challenges and dangers. The book is divided into three parts. The first part explores the intellectual, ethical and pragmatic contexts of PAR; the development and diversity of approaches to PAR; recent poststructuralist perspectives on PAR as a form of power; the ethic of participation; and issues of safety and well-being. Part two is a critical exploration of the politics, places and practices of PAR. Contributors draw on diverse research experiences with differently situated groups and issues including environmentally sustainable practices, family livelihoods, sexual health, gendered experiences of employment, and specific communities such as people with disabilities, migrant groups, and young people. The principles, dilemmas and strategies associated with participatory approaches and methods including diagramming, cartographies, art, theatre, photovoice, video and geographical information systems are also discussed. Part three reflects on how effective PAR is, including the analysis of its products and processes, participatory learning, representation and dissemination, institutional benefits and challenges, and working between research, action, activism and change.
The authors find that a spatial perspective and an attention to scale offer helpful means of negotiating the potentials and paradoxes of PAR. This approach responds to critiques of PAR by highlighting how the spatial politics of practising participation can be mobilised to create more effective and just research processes and outcomes. The book adds significant weight to the recent critical reappraisal of PAR, suggesting why, when, where and how we might take forward PAR’s commitment to enabling collaborative social transformation. It will be particularly useful to researchers and students of Human Geography, Development Studies and Sociology.
Tuesday, February 23, 2010
Ethics are central to community-based mapping processes
Dr. Nigel Crawhall, Director of Secretariat at the Indigenous Peoples of Africa Coordinating Committee (IPACC), a pan-African network, elaborates on the value of ethics in the context of participatory mapping processes.
More on practical ethics in PPGIS/PGIS practice is found here.
Sunday, February 21, 2010
Mapping the Sea - Improving Livelihoods
In 2005, when the Tsunami hit Banda Aceh in Indonesia, it killed many of the elderly fishermen. Much of the traditional knowledge about the waters surrounding Banda Aceh was lost with them. Traditionally this precious knowledge was transferred from generation to generation. In the post-Tsunami vacuum, this community-led initiative was able to retrieve and document some of that endangered knowledge.
This video documents the efforts done in one community, where traditional authorities coordinated the mapping of the coastal waters including the sea floor. So far 460 km of coastline have been mapped including previously unmapped features like four seamounts, four geologic faults and eighteen coral areas. In addition to the physical data, the community documented key biodiversity areas including shark nurseries, nesting beaches, spawning grounds. Data will be used to support the development of coastal resources and fisheries management plans.
According to Sumatra Konservasi Alam this project was completed at minimal cost (less than 10% of the cost of a conventional survey) and in less than one year. More information on the initiative is found at http://www.konservasi.org
Monday, February 08, 2010
Knowledge and cultural transmission in Kenyan participatory mapping
In this 5 minute interview Dr. Nigel Crawhall, Director of Secretariat at IPACC, elaborates on intergenerational ecological knowledge transmission in Participatory 3-dimensional modelling (P3DM). Crawhall discusses his observations on intergenerational interaction when the Ogiek community of Nessuit, Kenya built a geo-referenced model of their mountain forest landscape in 2006.
Saturday, January 30, 2010
Indigenous People’s Exchanges Amongst Philippines and Peru Promoted by CBCD and ALDAW
 The establishment of this linkage took place right at the time when indigenous peoples of the Amazonian Peru had began various forms of open resistance against hydrocarbon extraction in their traditional territories. The solidarity link between the IPs of Peru and Palawan is being consolidated through the collaboration of the Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW), the Peoples and Plants International (PPI) and, specifically, through the personal efforts of Dr. Miguel Alexiades (CBCD staff and PPI co-director). Such exchange promotes the sharing of experiences as a way of 1) fostering reflection and joint actions through the establishment of strategic alliances; and 2) addressing common problems regarding indigenous links, rights and claims over ancestral homelands and cultural landscapes.
The establishment of this linkage took place right at the time when indigenous peoples of the Amazonian Peru had began various forms of open resistance against hydrocarbon extraction in their traditional territories. The solidarity link between the IPs of Peru and Palawan is being consolidated through the collaboration of the Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW), the Peoples and Plants International (PPI) and, specifically, through the personal efforts of Dr. Miguel Alexiades (CBCD staff and PPI co-director). Such exchange promotes the sharing of experiences as a way of 1) fostering reflection and joint actions through the establishment of strategic alliances; and 2) addressing common problems regarding indigenous links, rights and claims over ancestral homelands and cultural landscapes. The envisaged goal is to enable the production of jointly produced video materials that could be used to exert pressure at a national and international policy level.
The envisaged goal is to enable the production of jointly produced video materials that could be used to exert pressure at a national and international policy level.Julio Cusurichi, representing the indigenous organization COINBAMAD (Consejo Indigena de la Cuenca Baja de Madre De Dios) and winner of the well-known award, the Goldman Prize - arrived in the Philippines on July 2009, leaving the country after 21 days. He traveled to Palawan (Philippines) accompanied by Dr. Novellino and the ALDAW (Ancestral Domain/Land Watch) staff. In Palawan, local indigenous organizations (Bangsa Palawan Philippines and NATRIPAL) facilitated the dialogue between Julio and different Palawan communities, while Dr. Novellino helped in the simultaneous translation from Spanish to Palawan language. During his stay, Julio met many indigenous leaders and communities’ members (including women and children) and shared his experience and lessons regarding the impacts of mining and other forms of commercial extractivism upon cultural landscapes and ancestral homelands. Participatory videos showing the impact of mining and oil extraction in Madre de Dios (Peru) have been shown also to the most isolated Palawan communities.
Through Julio’s visit, a process of direct exchange between grassroots indigenous mobilization in Madre de Dios, Peru and local indigenous anti-mining movements in Palawan has been initiated. Before Julio’s departure, this collaboration has been formalized in a Memorandum of Understanding. Video shootings made by Julio Cusurichi in Palawan have been taken back to Peru and will be shown to the Amazonian indigenous communities. A cross-visit of Palawan representatives to the Peruvian Amazon has been planned for the year 2010.
Saturday, January 23, 2010
Counter-mapping in the Philippines: The Gantong Geo-Tagged Report
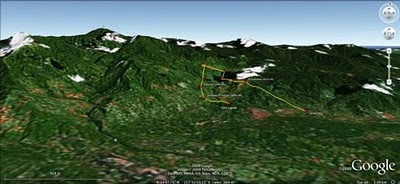 The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of two mining firms [MacroAsia and Celestial Nickel Mining and Exploration Corporation (CNMEC) now operated by Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC)] overlap with precious watersheds endowed with numerous creeks, springs and waterfalls providing potable water to the local indigenous communities and lowland farmers. More importantly, under the ECAN Guidelines of the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act 7611), such areas constitute the so called “core zones” of maximum protection where industrial extractive activities are not allowed.
The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of two mining firms [MacroAsia and Celestial Nickel Mining and Exploration Corporation (CNMEC) now operated by Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC)] overlap with precious watersheds endowed with numerous creeks, springs and waterfalls providing potable water to the local indigenous communities and lowland farmers. More importantly, under the ECAN Guidelines of the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act 7611), such areas constitute the so called “core zones” of maximum protection where industrial extractive activities are not allowed.At an altitude of about 500m ASL the mission reached indigenous settlements inhabited by very traditional Palawan having limited contacts with the outside. Their sustenance totally depends on the available forest resources, and it consists of a heterogeneous economy where sustainable swidden cultivation is integrated with foraging and the collection of non-timber forest products (NTFPs).
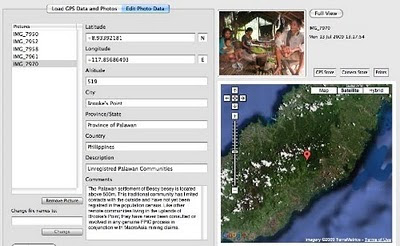
Overall, the mission moved from an elevation of a few meters ASL to an altitude of about 670m ASL, where one of the furthermost Palawan settlements is located. The mission’s GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of the JOBO GPS device being connected to the camera’s hot shoe. Positions were taken at intervals of several meters in order to reconstruct the mission’s full itinerary. The geo-tagged images were then loaded into ‘Photo GPS Editor’ and displayed on satellite Google map. All upland Palawan interviewed during the ALDAW/CBCD mission have declared that they have never been consulted about the entrance of mining companies in their traditional territories.

According to indigenous representatives, the Palawan branch of the National Commission on Indigenous Peoples (NCIP) – the government body mandated to ‘protect and promote the interest and well-being of cultural communities’ – is now siding with the mining companies. It is hoped that the ALDAW/CBCD Gantong geo-tagged report will facilitate the circulation of information, at both the national and international levels, on the threats faced by ‘irresponsible mining’ in the Philippines’ “last frontier”. An international campaign to support indigenous Palawan claims to their ancestral land has also been initiated by Survival International.
Source: The ALDAW NETWORK

The ALDAW NETWORK (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) is an advocacy-campaign network of Indigenous Peoples jointly constituted by NATRIPAL (United Tribes of Palawan) and BANGSA PALAWAN PHILIPPINES (Indigenous Alliance for Equity and Wellbeing) on August 2009.
Friday, January 08, 2010
Interview with Steve deRoy about the role of networking and communication in PGIS practice
In this interview, Mr. Steven DeRoy illustrates the power of networking and the importance of integrating this practice into the daily realm of PGIS. These professional exchanges create an opportunity to dialogue with likeminding professionals, allowing practitioners to share ideas and approaches to solve common challenges. Maps also play a vital role in communicating ideas amongst different parties and for advocating change in current affairs
Friday, October 23, 2009
Dr. Robert Chambers elaborates on Participatory GIS (PGIS) practice
Dr. Robert Chambers from the Institute of Development Studies (IDS), UK, reflects on the intersection of participatory development and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and on the resulting good and bad practices. In the interview Dr. Chambers calls on practitioners and development agencies to ensure that good practice is put in place to avoid the repetition of the misuse of PRA (i.e. Participatory Rural Appraisal) done in the 80's and 90's.
Thursday, October 22, 2009
The future of environmental law mapping
 Laurent Granier from ecocy recently wrote an essay on the future of environmental law mapping where he argues GIS and mapping tools are transforming our vision of legal data, “from vertical books to horizontal maps”. Drawing on examples of online mapping tools and representations, including participatory GIS, he shows a tendency for law and policy makers to aggregate administrative and legal layers in maps, towards more and more legally binding tools.
Laurent Granier from ecocy recently wrote an essay on the future of environmental law mapping where he argues GIS and mapping tools are transforming our vision of legal data, “from vertical books to horizontal maps”. Drawing on examples of online mapping tools and representations, including participatory GIS, he shows a tendency for law and policy makers to aggregate administrative and legal layers in maps, towards more and more legally binding tools.
Saturday, October 17, 2009
Educational Video ob CyberTracker - Tracking in the Cyber Age
The CTA recently released an educational video on CyberTracker technology. The video has been produced in the context of the development of a training kit aimed at supporting the spread of good practice in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information. This 8-min video on CyberTracker covers a number of uses to which geospatial information technology (GIT) can be put to work in the contexts of development and conservation.
CyberTracker is an open-source software developed in South Africa by the Cybertracker Conservation with financial support initially provided of by the European Commission. It can be installed on a GPS-enabled handheld device such as a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) or a Smartphone to collect geo-referenced data with detailed digital notation. It is a highly efficient way to gather large quantities of geo-coded field observations at a speed and level of detail not possible before. CyberTracker allows users to customise the interface to meet data collection needs. Screen designs can combine text and icons to optimise efficiency and customisation. The CyberTracker icon interface was originally designed for trackers who could not read or write. Nowadays all users including scientists and conservationists benefit from the icon-based interface because it enables significantly faster data entry.
Thursday, October 01, 2009
Francis Kakwetin Lesingo reports on the use of a 1:10,000 scale 3D model in Nessuit Kenya
Mr. Francis Kakwetin Lesingo - a representative from the Ogieks living in the Mau complex (Nakuru,Kenya) - reports back on the use of a 1:10,000 scale georeferenced physical 3d model manufactured by 26 ogiek clans in 2006 and 2007 in Nessuit Kenya. The initiative has benefitted from technical and financial assistance provided by CTA, Ermis Africa, the Indigenous Peoples of Africa Coordinating Committee (IPACC) and the Gaia Foundation UK.
Wednesday, September 30, 2009
The Touch Table for participatory land use planning
This video shows how the Touch Table can be used to support land use planning with multiple stakeholders with multiple interests
Friday, September 18, 2009
Applications of GIS in Community Forestry: Linking Geographic Information Technology to Community Participation

Wednesday, September 16, 2009
Head teacher Julius Sangogo reports on the usefullness of a Participatory 3D Model (P3DM) in Nessuit, Kenya
Head teacher Julius Sangogo reports on the usefullness of a Participatory 3D Model in Nessuit, Kenya from CTA on Vimeo.
Three years after the completion of a Participatory 3D model in Nessuit Kenya, head teacher Julius Sangogo recalls the uses of the model by local, national and international agencies and more importantly by the pupils of the local primary school.
Wednesday, September 09, 2009
Participatory 3D Model (P3DM) of Chivoko village, Solomon Islands
 A total of 60 representatives from the Chivoko community including youth, elders, women and men, students and chiefs; representatives from "Sasamunga Live and Learn", The Nature Conservancy (TNC), the "Lauru Land Conference of Tribal Communities" (LLCTC), and the Choiseul Provincial Fisheries constructed a 1:20,000 scale Participatory 3D Model (P3DM) of Chivoko village in the Tavula ward, Choiseul Province, Solomon Islands. The model covering a total area of 192 sq km is the 1st if its kind in Solomon Islands.
A total of 60 representatives from the Chivoko community including youth, elders, women and men, students and chiefs; representatives from "Sasamunga Live and Learn", The Nature Conservancy (TNC), the "Lauru Land Conference of Tribal Communities" (LLCTC), and the Choiseul Provincial Fisheries constructed a 1:20,000 scale Participatory 3D Model (P3DM) of Chivoko village in the Tavula ward, Choiseul Province, Solomon Islands. The model covering a total area of 192 sq km is the 1st if its kind in Solomon Islands.Tuesday, September 01, 2009
Qualitative GIS: A Mixed Methods Approach
 'Qualitative GIS is coming of age, and this definitive collection explains why it deserves broad attention. These carefully selected essays by leading researchers, organized around a broad conception of qualitative GIS that extends beyond multi-media data integration to embrace new software tools and interpretive, situated epistemologies, will push readers to rethink not only their preconceptions about qualitative GIS, but also about GI science and critical GIS. GIS researchers, practitioners, observers and users will find much to chew on here' - Professor Eric Sheppard, University of Minnesota, USA
'Qualitative GIS is coming of age, and this definitive collection explains why it deserves broad attention. These carefully selected essays by leading researchers, organized around a broad conception of qualitative GIS that extends beyond multi-media data integration to embrace new software tools and interpretive, situated epistemologies, will push readers to rethink not only their preconceptions about qualitative GIS, but also about GI science and critical GIS. GIS researchers, practitioners, observers and users will find much to chew on here' - Professor Eric Sheppard, University of Minnesota, USA Geographic Information Systems are an essential tool for analyzing and representing quantitative spatial data. Qualitative GIS explains the recent integration of qualitative research with Geographical Information Systems
With a detailed contextualising introduction, the text is organised in three sections:
Representation: examines how researchers are using GIS to create new types of representations; working with spatial data, maps, and othervisualizations to incorporate multiple meanings and to provide texture and context. This section includes a chapter by Jon Corbett and Giacomo Rambaldi dealing with participatory mapping by the title: "Geographic information technologies, local knowledge, and change (pages 75-91).
Analysis: discusses the new techniques of analysis that are emerging at the margins between qualitative research and GIS, this in the wider context of a critical review of mixed-methods in geographical research
Theory: questions how knowledge is produced, showing how ideas of 'science' and 'truth' inform research, and demonstrates how qualitative GIS can be used to interrogate discussions of power, community, and social action
Making reference to representation, analysis, and theory throughout, the text shows how to frame questions, collect data, analyze results, and represent findings in a truly integrated way. An important addition to the mixed methods literature, Qualitative GIS will be the standard reference for upper-level students and researchers using qualitative methods and Geographic Information Systems.
Available from Amazon.com (US) and Amazon.co.uk (Europe)
Thursday, June 11, 2009
Sculpture and Science help in Planning to Preserve The Mutton Hole Wetlands in Australia
 A 3D model of the Mutton Hole Wetlands near Normanton has been developed as a starting point for community consultation and discussion about how best to preserve and use the Mutton Hole Wetlands.
A 3D model of the Mutton Hole Wetlands near Normanton has been developed as a starting point for community consultation and discussion about how best to preserve and use the Mutton Hole Wetlands.The Mutton Hole Wetlands are situated just to the North and West of Normanton, and are a part of the Southern Gulf Aggregation, the largest continuous wetland of its type in northern Australia. Being vital for bird migration routes across northern Australia, the Southern Gulf Aggregation is considered to be of state, national and international significance.
In the past the wetlands formed part of the neighbouring Mutton Hole cattle station, but the area was declared a Conservation Park in 2004. Currently managed by Queensland Parks and Wildlife, Carpentaria Shire Council has been considering managing the park themselves. As a part of this consideration the Northern Gulf Resource Management Group has gained funding to write a management plan for the wetland.
 The management plan will highlight Aboriginal culture as well as the environmental values of the wetland in a plan to conserve it for future generations. There is strong support from the scientific and local community for use of the wetlands for bird watching, teaching and eco-tourism. As a step towards greater community consultation a model of the wetland area was built and is now located in the Normanton Visitor Information Centre (Burns Philp Building).
The management plan will highlight Aboriginal culture as well as the environmental values of the wetland in a plan to conserve it for future generations. There is strong support from the scientific and local community for use of the wetlands for bird watching, teaching and eco-tourism. As a step towards greater community consultation a model of the wetland area was built and is now located in the Normanton Visitor Information Centre (Burns Philp Building).Over six weeks in April and May 2009 students and staff from Normanton State School and the Gulf Christian College worked together with Dr Isla Grundy of CSIRO to construct a 3D model of the Mutton Hole Wetlands, using a technique called Participatory 3D Modelling (P3DM).
The model was made by first tracing the image of the wetlands from a 1:9500 satellite image onto a large piece of cardboard, then other features were added on or cut out. Finally, the rest of the landscape was painted onto the cardboard and the boundary of the Conservation Park marked with thread.
P3DM is a relatively new technique developed in the Philippines to support collaborative resource use and management, aimed to facilitate community participation in problem analysis and decision-making. This is the first time this participatory technique has been used to make a landscape model from cardboard in Australia.
 Since mid-May 2009 the model has been displayed at the Normanton Visitors Information Centre and on Thursday 21st May there was a formal public opening when students, parents and interested community members came to see what the schools had been working on. The exhibition was opened by Vicki Jones of Northern Gulf, along with Isla Grundy of CSIRO and Agnes Hughes from Normanton State School. The forty or so people who attended were able to take a closer look at the model and discuss wetland history and potential use. The community at large was invited to give it’s opinions and ideas on how the Mutton Hole Wetlands should be managed and used in the future through individual community consultations and group discussions held at the Information Centre.
Since mid-May 2009 the model has been displayed at the Normanton Visitors Information Centre and on Thursday 21st May there was a formal public opening when students, parents and interested community members came to see what the schools had been working on. The exhibition was opened by Vicki Jones of Northern Gulf, along with Isla Grundy of CSIRO and Agnes Hughes from Normanton State School. The forty or so people who attended were able to take a closer look at the model and discuss wetland history and potential use. The community at large was invited to give it’s opinions and ideas on how the Mutton Hole Wetlands should be managed and used in the future through individual community consultations and group discussions held at the Information Centre.Community Agro-Ecologist CSIRO Sustainable Ecosystems,
JCU / CSIRO Tropical Landscapes Joint Venture
Australian Tropical Forest Institute, James Cook University, Cairns, QLD 4870
Monday, May 04, 2009
Participatory 3D Modelling in Bale, Ethiopia
 MELCA Mahiber, an Ethiopian NGO member of the African Biodiversity network (ABN), facilitated the construction of a large Participatory 3D Model covering 1,575 sq. km (at a 1:12,500-scale) in Bale and West Arsi, Ethiopia.
MELCA Mahiber, an Ethiopian NGO member of the African Biodiversity network (ABN), facilitated the construction of a large Participatory 3D Model covering 1,575 sq. km (at a 1:12,500-scale) in Bale and West Arsi, Ethiopia.The exercise has been done to assist local communities in planning out a more sustainable management of the area, reviving local bio-cultural diversity and supporting local environmental education.
More information on the exercise is found here.
