Sunday, June 13, 2010
RROMUEPATSRO: Mapping the Historical-Cultural Space of the Yanesha, Perú
This video is the first in a series titled “Where Our Ancestors Walked: Mapping the Historical-Cultural Space of the Yanesha People,” which was made in collaboration with the Yanesha people in order to preserve their history and its relation with their territory as sacred landscape. Rromuepatsro presents the Yanesha people, located in the eastern slope of the Peruvian central Andes, and explores their vital relationship with their ancestors and the natural landscape. It shows how they have used PGIS, anthropological research and Yanesha oral history to map their historical cultural space and thus reaffirm their millennial link to the ancient world and the civilization of the central Andes.
This video has been produced in Spanish and English by the Instituto del Bien Común (IBC), Lima, Perú.
Wednesday, June 09, 2010
Reviving our culture, Mapping our future
The story of a special gathering in Venda, South Africa, and a community process in eco-cultural mapping. Indigenous leaders from Altai (Russia) and the Colombian Amazon, and NGO representatives from South Africa, Kenya and Ethiopia, accompany Tshidvizhe community as they explore a simple yet powerful way to express the past and present of their territory and livelihoods onto hand-drawn maps. The maps highlight the importance of their culture, sacred sites and territory, and empower them to map the future they need to strive for.
Production: The Gaia Foundation, African Biodiversity Network (ABN), Mupo Foundation and the Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Co-operation ACP-EU (CTA).
Friday, June 04, 2010
Participatory mapping at IFAD
The second phase of the project has focused on participatory mapping. As a result IFAD published “Good Practices in Participatory Mapping” and the “IFAD Adaptive Approach to Participatory Mapping”.
The next phase is focusing is participatory monitoring and evaluation of participatory mapping processes.
Below are the main outcomes of the second phase:
- The International Fund for Agricultural Development (Corbett J. M.) (2009) “ Good practices in participatory mapping.” The International Fund for Agricultural Development, Rome, Italy. 55 pages.
- Le Fonds international de développement agricole (Corbett J. M.) 2009. Cartographie participative et bonnes pratiques. Le Fonds international de développement agricole (FIDA), Rome, Italie. 59 pages
- El Fondo Internacional de Desarrollo Agrícola (Corbett J.M) 2009. Buenas prácticas en cartografía participativa. Análisis preparado para el Fondo Internacional de Desarrollo Agrícola (FIDA). Roma, Italia. 59 paginas
- The International Fund for Agricultural Development (Corbett J. M.) (2010) “Adaptive Mapping: IFAD Design and Delivery of Participatory Mapping Projects.” The International Fund for Agricultural Development, Rome, Italy. pp. 47
Tuesday, June 01, 2010
Whose Map? | ¿De Quién Son Los Mapas? | à qui appartiennent les cartes ? English / français/ español
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
- Robert Chambers. 2006. Participatory Mapping and Geographic Information Systems: Whose Map? Who is Empowered and Who Disempowered? Who Gains and Who Loses? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-11
- Robert Chambers. 2006. El Mapeo Participativo Y Los Sistemas De Información Geográfica: ¿De Quién Son Los Mapas? ¿Quién Se Empodera Y Quién Se Desempodera? ¿Quién Gana Y Quién Pierde? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-14 - Traducido y publicado por: Centro Técnico para la Cooperación Agricultural y Rural ACP-EU (CTA), 2010. Con la autorización de: EJISDC
- Robert Chambers. 2006. Cartographie participative et systèmes d’information géographique : à qui appartiennent les cartes ? Qui en ressort renforcé, qui en ressort affaibli ? Qui gagne et qui perd ? EJISDC 25, 2, 1-14 - Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission d’EJISDC
Sunday, May 30, 2010
Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication in Developing Countries / English / Français / Español
PGIS practice is geared towards community empowerment through measured, demand-driven, user-friendly and integrated applications of geo-spatial technologies. GIS-based maps and spatial analysis thus become major conduits in the process. A good PGIS practice is embedded into long-lasting and locally driven spatial decision-making processes, is flexible, adapts to different socio-cultural and bio-physical environments, depends on multidisciplinary facilitation and skills and builds essentially on visual language. If appropriately utilized, the practice should exert profound impacts on community empowerment, innovation and social change. More importantly, by placing control of access and use of culturally sensitive spatial information in the hands of those who generated them, PGIS practice can protect traditional knowledge and wisdom from external exploitation.
Effective participation is the key to good PGIS practice. Whilst the focus of traditional GIS applications is often on the outcome, PGIS initiatives tend to emphasize the processes by which outcomes are attained. At times the participatory process can obfuscate systematic inequalities through unequal and superficial participation. For example, PGIS applications may be used to legitimise decisions which in fact were taken by outsiders. The process can also easily be hijacked by community elites. For PGIS practices to be successful, they must be placed in a well thought out and demand-driven process based on the proactive collaboration of the custodians of local and traditional knowledge and of facilitators skilled in applying PGIS and transferring technical know-how to local actors. Participation thus cuts across the process from gaining a clear understanding of the existing legal and regulatory frameworks, to jointly setting project objectives, defining strategies and choosing appropriate geo-spatial information management tools. The integrated and multifaceted nature of PGIS provides legitimacy for local knowledge and generates a great sense of confidence and pride which prepares participant communities in dealing with outsiders. The process is intended to build self-esteem, raise awareness about pressing issues in the community and produce concrete and sustainable spatial solutions.
Below is the original article published on EJISDC, an open access journal, and translations in French and Spanish done in the context of the development of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Managamant and Communication" soon to be published by CTA and IFAD.
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication in Developing Countries. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9 .
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Gestion Participative de l’information Géographique et de la Communication dans les Pays en Développement. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9. Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission d’EJISDC
- Rambaldi G., Kwaku Kyem A. P.; Mbile P.; McCall M. and Weiner D. 2006. Manejo y Comunicación de la Información Territorial en Forma Participativa en los Países en vía de Desarrollo. EJISDC 25, 1, 1-9. Traducido y publicado por: Centro Técnico para la Cooperación Agricultural y Rural ACP-EU (CTA), 2010. Con permiso de: EJISDC
Selected publications on the subject are available at www.gis4d.com
Thursday, May 27, 2010
PPgis.net Open Forum on Participatory Geographic Information Systems and Technologies

Monday, May 24, 2010
Mapping Indigenous Lands / Mapeo de tierras indígenas / Cartographier les territoires autochtones
Here are the links to the documents.
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapping Indigenous Lands. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Mapeo de tierras indígenas. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traducido y publicado por el Centro Técnico de Cooperación Agrícola y Rural (CTA), con autorización de ―Annual Review of Anthropology‖
- Mac Chapin, Zachary Lamb, and Bill Threlkeld. Cartographier les territoires autochtones. Annual Review of Anthropology 34 (2005) : 619-639 - Traduit et publié par le Centre Technique de Coopération Agricole et Rurale (CTA) avec la permission de « Annual Review of Anthropology »
Monday, May 17, 2010
Participatory Action Research Approaches and Methods: Connecting People, Participation and Place
This book captures these developments, exploring the justification, theorisation, practice and implications of PAR. It offers a critical introduction to understanding and working with PAR in different social, spatial and institutional contexts. The authors engage with PAR’s radical potential, while maintaining a critical awareness of its challenges and dangers. The book is divided into three parts. The first part explores the intellectual, ethical and pragmatic contexts of PAR; the development and diversity of approaches to PAR; recent poststructuralist perspectives on PAR as a form of power; the ethic of participation; and issues of safety and well-being. Part two is a critical exploration of the politics, places and practices of PAR. Contributors draw on diverse research experiences with differently situated groups and issues including environmentally sustainable practices, family livelihoods, sexual health, gendered experiences of employment, and specific communities such as people with disabilities, migrant groups, and young people. The principles, dilemmas and strategies associated with participatory approaches and methods including diagramming, cartographies, art, theatre, photovoice, video and geographical information systems are also discussed. Part three reflects on how effective PAR is, including the analysis of its products and processes, participatory learning, representation and dissemination, institutional benefits and challenges, and working between research, action, activism and change.
The authors find that a spatial perspective and an attention to scale offer helpful means of negotiating the potentials and paradoxes of PAR. This approach responds to critiques of PAR by highlighting how the spatial politics of practising participation can be mobilised to create more effective and just research processes and outcomes. The book adds significant weight to the recent critical reappraisal of PAR, suggesting why, when, where and how we might take forward PAR’s commitment to enabling collaborative social transformation. It will be particularly useful to researchers and students of Human Geography, Development Studies and Sociology.
Sunday, May 16, 2010
Choosing a participatory mapping method versus another
The choice of method should emanate predominantly from within the community . Participatory maps often represent a socially or culturally distinct understanding of land and seascapes and include information that is excluded from mainstream maps. These usually represent the views of the dominant sectors of society. Participatory maps can pose alternatives to the languages and images of the existing power structures and become a medium of empowerment by allowing local communities to represent themselves spatially.
For this reason, participatory maps should be made through an inclusive process at community level. The higher the level of participation by all members of the community, the more beneficial the outcome because the final maps, and related outputs like multimedia, will reflect the collective knowledge, concerns and aspirations.
In September 2010, CTA and IFAD will launch a Training Kit dedicated to “Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication” and having the specific objective of supporting the spread of good practice in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information. More information on the training kit will be made available on the Internet and on this blog.
Wednesday, May 12, 2010
Participatory Video Validates Geo-Tagging Evidences on Mining Threats to Palawan Ecology and Indigenous Livelihoods
May 2010
Between July and September 2009, a mission organized by the Philippines-based Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW) and the Centre for Biocultural Diversity (CBCD) at the University of Kent demonstrated how the ecological balance and the survival of vulnerable indigenous communities on Palawan Island (a “Man and Biosphere Reserve” program of UNESCO) is being threatened by the ongoing mining rush. The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of mining firms, such as MacroAsia and Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporations, overlap with precious watersheds and the so called “core zones” of maximum protection. During the mission indigenous communities were engaged in the making and editing of participatory videos.
Today the voices of these isolated Palawan communities are available through the following links:
http://www.youtube.com/user/ALDAWpalawan
http://vimeo.com/aldawnetwork
Wednesday, April 28, 2010
ILO Convention on indigenous and tribal peoples: a manual
The manual - dated 2003 - does not explain each article of the Convention. It focuses on key concepts such as, for example, human rights, culture,land, development, education and health.
Nor does it strictly follow the structure of the Convention. It is divided into different sections. Each section deals with a key concept.
For easy reference, the manual has included the article or articles of the Convention which are being discussed. There is a descriptive explanation of each article. Concepts are introduced by using examples and experiences from indigenous and tribal peoples. This is to demonstrate the articles of the Convention in a practical way. ILO also included diagrams and photographs which highlight and explain some important elements of the articles.
Wednesday, April 21, 2010
Rethinking the Power of Maps
 A contemporary follow-up to the bestselling Power of Maps, this book takes a fresh look at what maps do, whose interests they serve, and how they can be used in surprising, creative, and radical ways.
A contemporary follow-up to the bestselling Power of Maps, this book takes a fresh look at what maps do, whose interests they serve, and how they can be used in surprising, creative, and radical ways.In Rethinking the Power of Maps, Denis Wood describes how cartography facilitated the rise of the modern state and how maps continue to embody and project the interests of their creators. He demystifies the hidden assumptions of map making and explores the promises and limitations of diverse counter-mapping practices today.
Thought-provoking illustrations include U.S. Geological Survey maps; electoral and transportation maps; and numerous examples of critical cartography, participatory GIS, and map art.
Wednesday, March 24, 2010
Power of Maps: (Counter) Mapping for Conservation
The authors argue that in doing so enriches consideration of the power geometries of conservation cartographies by inviting fuller consideration of diverse species and landscapes, as well as enabling discussion of other representational and productive effects of conservation mappings. Once determined, how might conservation maps serve to naturalize certain spaces or boundaries as fixed, or contribute to certain socio-psychological understandings of conservation possibilities or outcomes?
In the closing sections, the authors invoke the idea of ‘counter-mapping’ to explore strategies that might redress these concerns. Possibilities range from efforts to adapt the form of protected areas to more critical approaches that question the appropriateness of territorial focus and mapping practices for conservation goals.
In conclusion, Harris and Hazen argue that theorizing power in human, other-than-human, and inter-species contexts is essential to understanding the power geometries of conservation mapping.
Citation: Leila M. Harris and Helen D. Hazen, 2006. Power of Maps: (Counter) Mapping for Conservation. ACME: An International E-Journal for Critical Geographies, 4 (1), 99-130
Thursday, March 04, 2010
Geographic Information Technology and local spatial knowledge
Louis Liebenberg, founder and developer of CyberTracker technology shares his views on the importance of maintaining local knowledge at the forefront and to beware of the fact that technology may seduce users at the cost of dis-empowering local knowledge holders. Louis further highlights the role of the "Training Kit on Participatory Spatial Information Management and Communication" in empowering the grassroots.
Thursday, February 25, 2010
Palawan, Voices from the lost frontier
In March 2006, the Philippines’ President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo has called for a revitalization of mining nation-wide. The future of Palawan, known as the Philippines’ “Last Frontier” is now under serious threat. The island was declared a “Man and Biosphere Reserve” by the UNESCO and it is also the home of vanishing and isolated indigenous communities. Despite the numerous policies and laws establishing the entire province as a protected area, Palawan is becoming one of the most attractive mining investments destinations. This documentary is the outcome of a joint effort of indigenous communities, farmers, local NGOs and international institutions.
Wednesday, February 24, 2010
Biocultural Diversity Conservation: A Global Sourcebook
 Biocultural Diversity Conservation:
Biocultural Diversity Conservation:A Global Sourcebook
By Luisa Maffi and Ellen Woodley
Publication date: 19th February 2010
'All of the world's cultures are utterly dependent upon the biodiversity among which they live. Each culture has developed ways of adapting to their biodiversity, drawing on nature for goods, services, inspiration, mythology, and much else besides. Biocultural Diversity Conservation is a treasure trove of the many approaches that have been taken by the world's diverse cultures to maintain the biological systems upon which they depend. This invaluable resource will certainly find great utility in all parts of the world and among many disciplines. '
Jeffrey A. McNeely, Senior Science Advisor, IUCN
'Here is a treasure trove of a book, one that will truly make a difference in the world. It represents a key milestone in our global understanding of the profound and inextricable links between cultural and biological diversity. Written by two of the leading lights in this new and growing field, it is filled with important information, case studies and analyses on a global scale.'
Nancy J. Turner, University of Victoria, Canada
'At long last: an authoritative guide to biocultural conservation. This is a splendid illumination of the intermingled diversity of culture and nature ... revealing and revolutionary.'
Thomas E. Lovejoy, Biodiversity Chair, The Heinz Center for Science, Economics and the Environment, USA
The field of biocultural diversity is emerging as a dynamic, integrative approach to understanding the links between nature and culture and the interrelationships between humans and the environment at scales from the global to the local. Its multifaceted contributions have ranged from theoretical elaborations, to mappings of the overlapping distributions of biological and cultural diversity, to the development of indicators as tools to measure, assess, and monitor the state and trends of biocultural diversity, to on-the-ground implementation in field projects.
This book is a unique compendium and analysis of projects from all around the world that take an integrated biocultural approach to sustaining cultures and biodiversity. The 45 projects reviewed exemplify a new focus in conservation: this is based on the emerging realization that protecting and restoring biodiversity and maintaining and revitalizing cultural diversity and cultural vitality are intimately, indeed inextricably, interrelated.
Tuesday, February 23, 2010
Ethics are central to community-based mapping processes
Dr. Nigel Crawhall, Director of Secretariat at the Indigenous Peoples of Africa Coordinating Committee (IPACC), a pan-African network, elaborates on the value of ethics in the context of participatory mapping processes.
More on practical ethics in PPGIS/PGIS practice is found here.
Sunday, February 21, 2010
Mapping the Sea - Improving Livelihoods
In 2005, when the Tsunami hit Banda Aceh in Indonesia, it killed many of the elderly fishermen. Much of the traditional knowledge about the waters surrounding Banda Aceh was lost with them. Traditionally this precious knowledge was transferred from generation to generation. In the post-Tsunami vacuum, this community-led initiative was able to retrieve and document some of that endangered knowledge.
This video documents the efforts done in one community, where traditional authorities coordinated the mapping of the coastal waters including the sea floor. So far 460 km of coastline have been mapped including previously unmapped features like four seamounts, four geologic faults and eighteen coral areas. In addition to the physical data, the community documented key biodiversity areas including shark nurseries, nesting beaches, spawning grounds. Data will be used to support the development of coastal resources and fisheries management plans.
According to Sumatra Konservasi Alam this project was completed at minimal cost (less than 10% of the cost of a conventional survey) and in less than one year. More information on the initiative is found at http://www.konservasi.org
Tuesday, February 16, 2010
Ogiek Indigenous Peoples Mapping their Lands
Julius Muchemi, Executive Director of ERMIS Africa, an NGO based in Kenya, reports on a Participatory 3D Modelling exercise which occurred in Nessuit, Kenya in August 2006. In the course of the exercise - attended by representatives from 21 Ogiek clans - an area of 52,800 ha was mapped at a scale 1:10,000. participants included close to 120 representatives from the different clans, men and women. Elders populated the model with their memories dating back to 1925 and reconstructed the landscape as it was at that time. The model displays 64 data layers including different types of areas, points and lines. In 2008 the Ogiek people expanded the coverage of the model to include further 40,000 ha.
Read more ...
Sunday, February 14, 2010
GIS for Emergency Preparedness and Health Risk Reduction
 Geographical Information Systems (GIS) have developed rapidly in recent years and now provide powerful tools for the capture, manipulation, integration, interrogation, modelling, analysis and visualisation of data -- tools that are already used for policy support in a wide range of areas at almost all geographic and administrative levels. This holds especially for emergency preparedness and health risk reduction, which are all essentially spatial problems. To date, however, many initiatives have remained disconnected and uncoordinated, leading to less powerful, less compatible and less widely implemented systems than might otherwise have been the case. The important matters discussed here include the probabilistic nature of most environmental hazards and the semi-random factors that influence interactions between these and human exposures; the effects of temporal and spatial scales on hazard assessment and imputed risk; the effects of measurement error in risk estimation and the stratification of risks and their impacts according to socioeconomic characteristics; and the quantification of socioeconomic differences in vulnerability and susceptibility to environmental hazards. GIS are powerful analytical tools in their own right, but what is needed is much more effective communication between the many disciplines, professions and stakeholders concerned -- something which this book helps to achieve.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) have developed rapidly in recent years and now provide powerful tools for the capture, manipulation, integration, interrogation, modelling, analysis and visualisation of data -- tools that are already used for policy support in a wide range of areas at almost all geographic and administrative levels. This holds especially for emergency preparedness and health risk reduction, which are all essentially spatial problems. To date, however, many initiatives have remained disconnected and uncoordinated, leading to less powerful, less compatible and less widely implemented systems than might otherwise have been the case. The important matters discussed here include the probabilistic nature of most environmental hazards and the semi-random factors that influence interactions between these and human exposures; the effects of temporal and spatial scales on hazard assessment and imputed risk; the effects of measurement error in risk estimation and the stratification of risks and their impacts according to socioeconomic characteristics; and the quantification of socioeconomic differences in vulnerability and susceptibility to environmental hazards. GIS are powerful analytical tools in their own right, but what is needed is much more effective communication between the many disciplines, professions and stakeholders concerned -- something which this book helps to achieve.
Wednesday, February 10, 2010
Report on the situation of human rights and fundamental freedoms of indigenous peoples in Kenya
I am quoting part of the text and offer a link to the full document at the bottom of this post.
...
C. Hunter-gatherers and forest peoples
36. Settlement schemes, logging and charcoal production have put a severe strain on Kenya’s rich and varied forests, and have resulted in the loss of the traditional habitat of Kenya’s forest peoples, the indigenous hunter-gatherers such as the Awer (Boni), Ogiek, Sengwer, Watta, and Yaaku. While existing laws are oriented to the protection of wildlife and forest resources, many of these communities can no longer live by their traditional livelihoods, and their cultures and language are rapidly vanishing as a result; illegal logging has played a major role in this as well.
37. The way of life of the Ogiek is well adapted to the Mau Forest environment where they have lived for centuries. Numbering about 20,000 countrywide, they have been dispersed and assimilated in recent decades, and dispossessed of their traditional source of livelihood. When the Mau Forest was gazetted as a National Forest in 1974, the Ogiek were evicted from their traditional habitat without prior consultation or compensation, in violation of their basic human rights. They were henceforth prevented from hunting or collecting bee honey for survival in the forest, and were reduced to a miserable subsistence on the margins of this area rich in plants and wildlife. On the other hand, illegal logging, the introduction of exotic plantations and the excision of parts of the forest for private development by outside settlers have endangered the Mau Forest as a water catchment area, as well as the country’s environmental security. The Special Rapporteur on adequate housing, Miloon Kothari, signalled in his report on his mission to Kenya that the destruction of the forest has affected the rights of the Ogiek to housing, health, food and a safe environment, threatening to further destroy their cultural identity and the community as a whole (see E/CN.4/2005/48/Add.2, para. 61).
38. Despite a court injunction in their favour in 1997, the Government has proceeded to alienate Ogiek forest land, and a recent court decision does not recognize the Ogiek’s ancestral title to the forest. Still, the Government has distributed title deeds to land to several thousand Ogiek, and some non-Ogiek outsiders have tried to enrol as Ogieks in the hope that they may eventually also be given title deeds. The unresolved conflict between the Ogiek and their neighbours continues to this day. Being considered as squatters on their own land and legally banned from using the forest resources for their livelihood, their attempt to survive according to their traditional lifestyle and culture has often been criminalized and their repeated recourse to the courts has not been successful. Ogiek attribute this vulnerability to the fact that they are not recognized as a distinct tribe and therefore lack political representation. The Special Rapporteur met with members of several Ogiek villages, listened to their grievances and heard their demands for the recognition of their right to land and to maintain their traditional lifestyle in the forest.
...
90. In view of the above, the Special Rapporteur makes the following recommendations:
A. Recommendations to the Government
...
Forest areas
102. The rights of indigenous hunter-gatherer communities (particularly the Ogiek in Mau Forest) to occupy and use the resources in gazetted forest areas should be legally recognized and respected. Further excisions of gazetted forest areas and evictions of hunter-gatherers should be stopped. Titles derived from illegal excision or allocation of forest lands should be revoked, and new titles should only be granted to original inhabitants. Illegal commercial logging should be stopped.
C. Recommendations to indigenous communities and organizations
...
124. Indigenous peoples’ organizations are encouraged to develop concrete strategies for data collection, research and documentation to support their advocacy work both at the national and international levels.
D. Recommendations to civil society and political parties
...
127. NGOs and donors should strengthen their relations with indigenous communities, support their development initiatives and promote a better understanding of their demands and aspirations within Kenyan society.
...
Read / download the full document.
Monday, February 08, 2010
Knowledge and cultural transmission in Kenyan participatory mapping
In this 5 minute interview Dr. Nigel Crawhall, Director of Secretariat at IPACC, elaborates on intergenerational ecological knowledge transmission in Participatory 3-dimensional modelling (P3DM). Crawhall discusses his observations on intergenerational interaction when the Ogiek community of Nessuit, Kenya built a geo-referenced model of their mountain forest landscape in 2006.
Sunday, February 07, 2010
Geographic Information Science and Public Participation
 Computer-mediated participation is at the crossroads. In the early heady days of the digital revolution, access to "high" technologies such as GIS promised the empowerment of marginalized communities by providing data and information that was previously hidden away from public view. To a great extent, this goal has been achieved at least in the U.S. and Western Europe – data about a range of government initiatives and raw data about different aspects of spatial planning such as land use, community facilities, property ownership are available a mouse-click away. Now, that the public, have access to information, are we able to make better plans for the future of our cities and regions? Are we more inclusive in our planning efforts? Are we able to foster collaborative governance structures mediated by digital technologies?
Computer-mediated participation is at the crossroads. In the early heady days of the digital revolution, access to "high" technologies such as GIS promised the empowerment of marginalized communities by providing data and information that was previously hidden away from public view. To a great extent, this goal has been achieved at least in the U.S. and Western Europe – data about a range of government initiatives and raw data about different aspects of spatial planning such as land use, community facilities, property ownership are available a mouse-click away. Now, that the public, have access to information, are we able to make better plans for the future of our cities and regions? Are we more inclusive in our planning efforts? Are we able to foster collaborative governance structures mediated by digital technologies?In Geographic Information Science and Public Participation (Advances in Geographic Information Science)
The foreword for the book is written by Prof. Bill Huxhold.
Tuesday, February 02, 2010
Digital Cartography
Digital Cartography from dynamicmediainstitute.org on Vimeo.
By Andrew Ellis, Alexander Wang, Students at the Dynamic Media Institute, Massachusetts College of Art and Design
Digital Cartography is a short documentary film on the transition of maps into their digital form. In this film we speak with programmer and mapmaker Jeffrey Warren from the MIT Media Lab and Dietmar Offenhuber from SENSEable City Lab at MIT. We explore the cultural, economic and technical aspects of mapmaking and how they affect the way we communicate with one another.
In our interviews with Jeffrey and Dietmar we learn about the social and geographical ramifications of building maps and how designers can implement their literacy in communication design to explore different avenues for mapping. Participatory mapping such as Open Street Maps and psychogeography and the virtual dérive are some of the themes discussed around the history and future of mapping in the digital age. Jeffrey gives us a demonstration on low cost arial photography using a helium balloon and a consumer digital camera to stitch photos onto google maps.
Metodología participativa para construir una maqueta 3D en Telpaneca, Nicaragua
El video es una producción de la Unión Nacional de Agricultores y Ganaderos (UNAG) de Nueva Segovia, y la ONG francesa Agrónomos y Veterinarios Sin Fronteras (AVSF).
Monday, February 01, 2010
Community Mapping in Tsunami Affected Areas in Aceh, Indonesia
The documentary has been jointly produced by the Indonesia Community Mapping Network or Jaringan Kerja Pemetaan Partisipatif (JKPP), and the Center for people Economic Development or Yayasan Rumpun Bambu Indonesia (YRBI).
More videos on participatory mapping are found here.
Sunday, January 31, 2010
CyberTracker releases a sample database for Disaster Relief Rapid Surveying
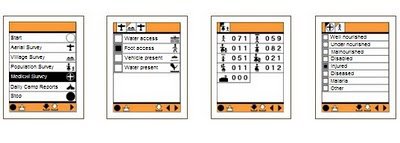 The CyberTracker software can be installed on GPS-enabled Windows Mobile smartphones.
The CyberTracker software can be installed on GPS-enabled Windows Mobile smartphones.This may help to gather crucial data required to co-ordinate disaster relief logistics.
One of the critical problems in disaster relief management is the lack of reliable data on basic needs on the ground after a major natural disaster. Disaster relief efforts must overcome serious logistical problems due to poor communication and unreliable information. Gathering good quality data on the ground will make it possible to make informed decisions on where the highest priorities are.
Better information on quantities of relief supplies needed, such as medicines, food, blankets, shelter and clothing will ensure that resources are used more efficiently where they are needed most.
Source: Louis Liebenberg, CyberTracker Conservation
Saturday, January 30, 2010
Indigenous People’s Exchanges Amongst Philippines and Peru Promoted by CBCD and ALDAW
 The establishment of this linkage took place right at the time when indigenous peoples of the Amazonian Peru had began various forms of open resistance against hydrocarbon extraction in their traditional territories. The solidarity link between the IPs of Peru and Palawan is being consolidated through the collaboration of the Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW), the Peoples and Plants International (PPI) and, specifically, through the personal efforts of Dr. Miguel Alexiades (CBCD staff and PPI co-director). Such exchange promotes the sharing of experiences as a way of 1) fostering reflection and joint actions through the establishment of strategic alliances; and 2) addressing common problems regarding indigenous links, rights and claims over ancestral homelands and cultural landscapes.
The establishment of this linkage took place right at the time when indigenous peoples of the Amazonian Peru had began various forms of open resistance against hydrocarbon extraction in their traditional territories. The solidarity link between the IPs of Peru and Palawan is being consolidated through the collaboration of the Ancestral Land/Domain Watch (ALDAW), the Peoples and Plants International (PPI) and, specifically, through the personal efforts of Dr. Miguel Alexiades (CBCD staff and PPI co-director). Such exchange promotes the sharing of experiences as a way of 1) fostering reflection and joint actions through the establishment of strategic alliances; and 2) addressing common problems regarding indigenous links, rights and claims over ancestral homelands and cultural landscapes. The envisaged goal is to enable the production of jointly produced video materials that could be used to exert pressure at a national and international policy level.
The envisaged goal is to enable the production of jointly produced video materials that could be used to exert pressure at a national and international policy level.Julio Cusurichi, representing the indigenous organization COINBAMAD (Consejo Indigena de la Cuenca Baja de Madre De Dios) and winner of the well-known award, the Goldman Prize - arrived in the Philippines on July 2009, leaving the country after 21 days. He traveled to Palawan (Philippines) accompanied by Dr. Novellino and the ALDAW (Ancestral Domain/Land Watch) staff. In Palawan, local indigenous organizations (Bangsa Palawan Philippines and NATRIPAL) facilitated the dialogue between Julio and different Palawan communities, while Dr. Novellino helped in the simultaneous translation from Spanish to Palawan language. During his stay, Julio met many indigenous leaders and communities’ members (including women and children) and shared his experience and lessons regarding the impacts of mining and other forms of commercial extractivism upon cultural landscapes and ancestral homelands. Participatory videos showing the impact of mining and oil extraction in Madre de Dios (Peru) have been shown also to the most isolated Palawan communities.
Through Julio’s visit, a process of direct exchange between grassroots indigenous mobilization in Madre de Dios, Peru and local indigenous anti-mining movements in Palawan has been initiated. Before Julio’s departure, this collaboration has been formalized in a Memorandum of Understanding. Video shootings made by Julio Cusurichi in Palawan have been taken back to Peru and will be shown to the Amazonian indigenous communities. A cross-visit of Palawan representatives to the Peruvian Amazon has been planned for the year 2010.
Saturday, January 23, 2010
Counter-mapping in the Philippines: The Gantong Geo-Tagged Report
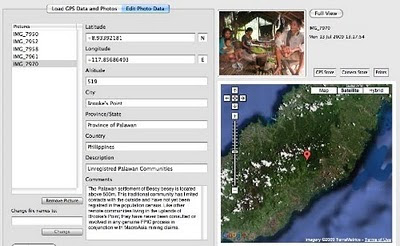
 The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of two mining firms [MacroAsia and Celestial Nickel Mining and Exploration Corporation (CNMEC) now operated by Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC)] overlap with precious watersheds endowed with numerous creeks, springs and waterfalls providing potable water to the local indigenous communities and lowland farmers. More importantly, under the ECAN Guidelines of the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act 7611), such areas constitute the so called “core zones” of maximum protection where industrial extractive activities are not allowed.
The mission’s actual ‘matching’ of collected GPS data to photographs shows that the Mineral Production Sharing Agreements (MPSA) of two mining firms [MacroAsia and Celestial Nickel Mining and Exploration Corporation (CNMEC) now operated by Ipilan Nickel Corporation (INC)] overlap with precious watersheds endowed with numerous creeks, springs and waterfalls providing potable water to the local indigenous communities and lowland farmers. More importantly, under the ECAN Guidelines of the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act 7611), such areas constitute the so called “core zones” of maximum protection where industrial extractive activities are not allowed.At an altitude of about 500m ASL the mission reached indigenous settlements inhabited by very traditional Palawan having limited contacts with the outside. Their sustenance totally depends on the available forest resources, and it consists of a heterogeneous economy where sustainable swidden cultivation is integrated with foraging and the collection of non-timber forest products (NTFPs).
Overall, the mission moved from an elevation of a few meters ASL to an altitude of about 670m ASL, where one of the furthermost Palawan settlements is located. The mission’s GPS coordinates were obtained through the use of the JOBO GPS device being connected to the camera’s hot shoe. Positions were taken at intervals of several meters in order to reconstruct the mission’s full itinerary. The geo-tagged images were then loaded into ‘Photo GPS Editor’ and displayed on satellite Google map. All upland Palawan interviewed during the ALDAW/CBCD mission have declared that they have never been consulted about the entrance of mining companies in their traditional territories.

According to indigenous representatives, the Palawan branch of the National Commission on Indigenous Peoples (NCIP) – the government body mandated to ‘protect and promote the interest and well-being of cultural communities’ – is now siding with the mining companies. It is hoped that the ALDAW/CBCD Gantong geo-tagged report will facilitate the circulation of information, at both the national and international levels, on the threats faced by ‘irresponsible mining’ in the Philippines’ “last frontier”. An international campaign to support indigenous Palawan claims to their ancestral land has also been initiated by Survival International.
Source: The ALDAW NETWORK

The ALDAW NETWORK (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) is an advocacy-campaign network of Indigenous Peoples jointly constituted by NATRIPAL (United Tribes of Palawan) and BANGSA PALAWAN PHILIPPINES (Indigenous Alliance for Equity and Wellbeing) on August 2009.
Friday, January 22, 2010
Peter Poole traces the evolution of participatory map-making
In this interview, Dr. Peter Poole traces the evolution of a participatory map-making which commenced with the introduction of GPS to the Inuits in 1989 and evolved throughout the 1990s via a series of projects in the Amazon, the Arctic and Asia.
Tenure maps depict indigenous names, resources and special places on scaled maps, intended as evidence in negotiating processes. Peter describes the search for cheap, simple, appropriate geomatic technology. Community-based teams would gather raw field data and indigenous associations or support NGOs, set up mapping units to serve the field teams.
Three lessons are described: (i) communities can make their own scaled maps, (ii) emerging mapping centres should make their services accessible to all communities, (iii) this methodology not only produces a tenure map, but also equips and inspires community mappers to diversify their skills in environmental information management.
Thursday, January 21, 2010
The Bulanjao Geotagged Report
Geo-referenced audio-visual and photographic documentation was carried out in the Bulanjao range whose vegetation consists of a very unique type of forest growing on ultramafic /heavy-metal rich soils. The area is home to at least four plant species that are classified as vulnerable and two of them have already been included in the IUCN Red List.
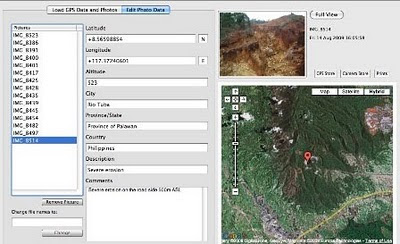 In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.
In spite of its unique ecological features, the Bulanjao range has been subjected to mineral exploration and development by the Rio Tuba Nickel Mining Corporation (RTNMC). RTNMC is a Filipino-Japanese partnership holding a mining concession area of about 5,265 hectares.RTNMC and its partner, Coral Bay Nickel Corporation (CBNC), need to mine nickel ores as part of the expansion of their new Hydrometallurgical Processing Plant (HPP) project. However, one the conditions specified in the Environmental Compliance Certificate (ECC) issued to them in 2002, is that “core zones” - as identified by the Strategic Environmental Plan for Palawan (Republic Act Republic Act 7611) should not be included in the areas of mining operations and, this, of course includes the Bulanjao range.
 Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.
Starting at an elevation of about 40m ASL, the ALDAW/CBCD mission followed the mining road to reach the highest portions of the Bulanjao range. Geo-tagging evidence indicates that erosion on the Bulanjao mining road is occurring also at low elevations. During the rainy season the water creates deep clefts on the roadsides, hence penetrating the soil and fostering road collapse. No mitigating measures have been put into place to reduce erosion. A huge crater-like excavation has been found at 566m ASL. and land slides, induced by road construction, have been documented around the sources of the Sumbiling river, at almost 900m ASL. The latter is the most important water source for both lowland farmers and indigenous communities.Marylin Samparan, a local IP living in the area told the mission: “time will come when our children will no longer recognize the names of trees, the footprints of animals, the birds’ songs. This will be the time when the forest will be gone, the mining companies will be gone, the rivers will no longer flow…and us? We will still be here”.
On 15 August 2009, the mission established that mining road had already reached an altitude of 859m ASL – and its exact location was defined through the following GPS coordinates (+ 8.59322548 N Latitude and + 117.36516571 E Longitude).
 Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.
Mission’s findings have now been compiled into a geo-tagged report, which is being used by local indigenous communities to support their legal struggle against mining in Bulanjao.Source: The ALDAW NETWORK
The ALDAW NETWORK (Ancestral Land/Domain Watch) is an advocacy-campaign network of Indigenous Peoples jointly constituted by NATRIPAL (United Tribes of Palawan) and BANGSA PALAWAN PHILIPPINES (Indigenous Alliance for Equity and Wellbeing) on August 2009.
Tuesday, January 19, 2010
What 3-D mapmakers should know about expanded EVA / PE closed-cell foam or sponge
 Expanded EVA / PE closed-cell foam or sponge is usually made out of a blend of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate copolymer (also known as EVA) and polyethylene. The product is a lightweight foam material which has a smooth surface and does not absorb water. Generally EVA sheeting is priced competitively, compared with other blown materials and is available in different densities, thicknesses and colours.
Expanded EVA / PE closed-cell foam or sponge is usually made out of a blend of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate copolymer (also known as EVA) and polyethylene. The product is a lightweight foam material which has a smooth surface and does not absorb water. Generally EVA sheeting is priced competitively, compared with other blown materials and is available in different densities, thicknesses and colours.It is one of the materials most popularly known as expanded rubber or foam rubber sheeting.
EVA foam is used to produce - among others - mouse pads, flip flops and sports mats. Sheets of the material can be used for manufacturing Participatory 3D Models.
Models made out of this material are well suited for humid tropical environments where carton board may deteriorate rapidly.
Manufacturing a 3D model using 'expanded EVA / PE closed-cell foam' compared to carton board implies a slightly higher cost and non biodegradable debris, but ensures a more durable output and a consistent vertical scale/exaggeration of the 3D model. Insertion of map and push pins is easy.
More information on the topic is found here.
Friday, January 08, 2010
Interview with Steve deRoy about the role of networking and communication in PGIS practice
In this interview, Mr. Steven DeRoy illustrates the power of networking and the importance of integrating this practice into the daily realm of PGIS. These professional exchanges create an opportunity to dialogue with likeminding professionals, allowing practitioners to share ideas and approaches to solve common challenges. Maps also play a vital role in communicating ideas amongst different parties and for advocating change in current affairs
Google Earth Outreach initiative in Africa
 Google Earth Outreach in Africa was recently launched with the objective of enabling non-profit and public benefit organizations in the continent to access the knowledge and resources they need to organize their data, build their maps, tell their stories through geographic visualization.
Google Earth Outreach in Africa was recently launched with the objective of enabling non-profit and public benefit organizations in the continent to access the knowledge and resources they need to organize their data, build their maps, tell their stories through geographic visualization.Monday, December 14, 2009
Community mapping in Borneo
 Community members and park naturalists have completed a participatory 3-dimensional scaled model of the Buayan-Kionop area showing areas important for community livelihoods. The pproject, funded by the Darwin Initiative, is designed to contribute to the nomination of the Crocker Range Biosphere Reserve. Work began in August 2009 with local partners and 10 indigenous communities. Local researchers from Buayan-Kionop are sharing their skills with neighbouring communities to document and map community livelihood patterns for the entire Ulu Papar area. They have been using a range of techniques, including participatory GIS and participatory 3-dimensional modelling (P3DM) to show areas important for cultivation, hunting, fishing and gathering of forest products. Over the next 3 years, we will build on the participatory research results in Buayan-Kionop and create spaces for community dialogue on balancing conservation and sustainable resource use in the Crocker Range.
Community members and park naturalists have completed a participatory 3-dimensional scaled model of the Buayan-Kionop area showing areas important for community livelihoods. The pproject, funded by the Darwin Initiative, is designed to contribute to the nomination of the Crocker Range Biosphere Reserve. Work began in August 2009 with local partners and 10 indigenous communities. Local researchers from Buayan-Kionop are sharing their skills with neighbouring communities to document and map community livelihood patterns for the entire Ulu Papar area. They have been using a range of techniques, including participatory GIS and participatory 3-dimensional modelling (P3DM) to show areas important for cultivation, hunting, fishing and gathering of forest products. Over the next 3 years, we will build on the participatory research results in Buayan-Kionop and create spaces for community dialogue on balancing conservation and sustainable resource use in the Crocker Range.More information on the programme is found here.
Source: Agnes Lee Agama, Southeast Asia coordinator, Global Diversity Foundation update December 2009
Friday, November 27, 2009
Eco-cultural mapping to protect natural resources and sacred sites, South Africa
 With support from CTA, women, men and youth from Tshidzivhe community, in Limpopo province, northern South Africa, spent six days exploring ways to ‘map’ their traditional knowledge and practices for managing their natural resources. As the different maps were finished, the local people celebrated their new capacity to express traditional environmental knowledge in an appropriate way for gaining recognition, reviving traditional practices and securing their rights.
With support from CTA, women, men and youth from Tshidzivhe community, in Limpopo province, northern South Africa, spent six days exploring ways to ‘map’ their traditional knowledge and practices for managing their natural resources. As the different maps were finished, the local people celebrated their new capacity to express traditional environmental knowledge in an appropriate way for gaining recognition, reviving traditional practices and securing their rights.This was a unique mapping experience that involved local people as well as indigenous from other parts of the world. More than 70 vhaVenda people took part, guided by trainers in eco-cultural mapping from Colombia and accompanied by indigenous leaders from the Colombian Amazon and the Russian Republic of Altai. The process required the full participation of community members, especially the elders and the makhadzis, women custodians of sacred sites, but with minimal materials or technology.
 Four maps and two ecological calendars were produced, covering what the local population refers to as “Venda territory” and with special attention to the main sacred sites. The maps show the changes and alterations to the land - the past, present and future visions - and the importance of recovering traditional practices and rituals.
Four maps and two ecological calendars were produced, covering what the local population refers to as “Venda territory” and with special attention to the main sacred sites. The maps show the changes and alterations to the land - the past, present and future visions - and the importance of recovering traditional practices and rituals.Trainees from Kenya and Ethiopia, members of the African Biodiversity Network, took part and hope to carry out similar workshops in their respective countries in 2010.
Photos by Will Baxter, text by Fiona Wilton / The Gaia Foundation
Saturday, November 21, 2009
Ogieks will not be evicted from the Mau forest
As reported by NTVKenya on October 24, 2009 , it is emerging that members of the Ogiek indigenous community will not be affected by the eviction notice. the Mau task force committee says the indigenous forest dwellers will not be moved when the evictions start soon. The announcement came as the Prime Minister gunned for more financial support for the Mau in Europe.
Related news and actions on PPgis.Net Blog:
Ogiek Appeal to the Kenya Government Notice to vacate Mau Forest Complex and other water towers
The 2009 UNESCO World Report on Cultural Diversity makes reference to the Ogiek 3D Mapping
Francis Kakwetin Lesingo reports on the use of a 1:10,000 scale 3D model in Nessuit Kenya
More on indigenous mapping by Ogiek People in the Mau Forest
Friday, November 13, 2009
Peter Poole reports on his experience with community mapping
In this interview, Peter Poole traces the evolution of a map-making methodology which commenced with his introduction of GPS to the Inuit community of Pangnirtung in 1989 and was incubated throughout the 1990’s by a series of ‘tenure mapping’ projects in the Amazon the Arctic and Asia. Tenure maps depict indigenous names, resources and special places on scaled maps, intended as evidence in negotiating land settlements.
Most tenure mapping methods rely upon external cartographic expertise. The “no-name” method enables communities to control the complete information cycle: gathering raw data, their conversion to information, its application.
The interview describes the search for cheap, simple, appropriate geomatic technology.
During several tenure mapping projects in the Amazon, a two-tier arrangement evolved whereby community-based teams would gather raw field data, the most critical task, and indigenous associations or support NGO’s, set up mapping units to serve the field teams.
The interview shifts focus to an overview of global community mapping completed by Peter Poole. In this, he concluded that, in terms of expertise, accessibility and accomplishment, the Philippines. He also drew a broad distinction to tenure mapping in America, a continent whose indigenous peoples sharing a in common ‘500 years since Columbus’ experience, and Africa, where this model does not work and where community mapping is taking off in a refreshing variety of directions.
The interview concludes with three lessons learned:
- Yes, communities can make their own scaled maps.
- The most successful of emerging mapping centres are those whose services are accessible to all communities.
- This capacity-building approach to map making equips and inspires people to diversify their skills in environmental information management. These skills will be wasted unless provisions are made to follow up tenure mapping projects with either further training or employment.
Saturday, November 07, 2009
Friday, November 06, 2009
Dave De Vera elaborates on Participatory GIS practice in the Philippines
Dave De Vera is the Executive Director of the Philippine Association For Intercultural Development (PAFID). In his interview Dave elaborates on the use of Participatory GIS practice in the Philippines to support indigenous communities in filing ancestral land claims. He elaborates on the mapping methods used, explains why P3DM is the most effective, and arguments on the need for local ownership of the process, competency of the technology intermediary, quality work, and constructive relationships with Government. Dave further lists cases of PAFID / Government partnerships and analyses the pillars of process legitimization.
Indigenous Peoples in Africa prepare for Copenhagen - REDD and human rights
Delegates emphasised that indigenous peoples are important stakeholders in climate stabilisation in Africa. Indigenous leaders must educate their communities as to the causes and engage with national governments about equitable and sustainable responses. Delegates reported back on mitigation / REDD (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) workshops that were held this year in Cape Town, Kampala, Nanyuki (Kenya) and Libreville, Gabon. The primary issues were to promote a fair and community-focused approach to REDD plus financing for forest conservation in Africa.
Government forestry officials from Uganda and Kenya gave presentations on how their governments are contracting with local communities to conserve tropical forests, and introduce new forms of carbon financing.
Jeniffer Koinante, Deputy Chairperson of IPACC gave a presentation on how the forest-based indigenous peoples of Kenya are using Participatory 3-Dimensional Models (P3DM) to help them review traditional adaptation customs, knowledge and practices, which could be harnessed to strengthen resilience of ecosystems and communities in the face of climate change.
Saturday, October 24, 2009
The UNESCO World Report on Cultural Diversity makes reference to P3DM done by Ogiek Peoples
 The 420-page UNESCO World Report on Cultural Diversity has been launched by the Director-General, to the attention of the Permanent Delegates to the 35th session of the General Conference, on Tuesday 20 October 2009.
The 420-page UNESCO World Report on Cultural Diversity has been launched by the Director-General, to the attention of the Permanent Delegates to the 35th session of the General Conference, on Tuesday 20 October 2009.The use of participatory three-dimensional modelling (P3DM) by the Ogiek Peoples in Kenya is cited in section 2.4 as an example of local Empowerment (see page 52 of the report).
Specifically the report makes reference to the article published by Rambaldi et al. on Information Development in 2007: Through the eyes of hunters-gatherers: Participatory 3D modelling among the Ogiek indigenous peoples in Kenya.
It is worth noting that the power of participatory mapping coupled with Web 2.0 commnunication tools (ppgis list, blog, YouTube, etc) coupled with actions undertaken by concerned stakeholders, have raised the concerns faced by a minority group like the Ogiek at the forefront of public opinion.
Friday, October 23, 2009
Dr. Robert Chambers elaborates on Participatory GIS (PGIS) practice
Dr. Robert Chambers from the Institute of Development Studies (IDS), UK, reflects on the intersection of participatory development and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and on the resulting good and bad practices. In the interview Dr. Chambers calls on practitioners and development agencies to ensure that good practice is put in place to avoid the repetition of the misuse of PRA (i.e. Participatory Rural Appraisal) done in the 80's and 90's.
Thursday, October 22, 2009
The future of environmental law mapping
 Laurent Granier from ecocy recently wrote an essay on the future of environmental law mapping where he argues GIS and mapping tools are transforming our vision of legal data, “from vertical books to horizontal maps”. Drawing on examples of online mapping tools and representations, including participatory GIS, he shows a tendency for law and policy makers to aggregate administrative and legal layers in maps, towards more and more legally binding tools.
Laurent Granier from ecocy recently wrote an essay on the future of environmental law mapping where he argues GIS and mapping tools are transforming our vision of legal data, “from vertical books to horizontal maps”. Drawing on examples of online mapping tools and representations, including participatory GIS, he shows a tendency for law and policy makers to aggregate administrative and legal layers in maps, towards more and more legally binding tools.
Sunday, October 18, 2009
Pister la Vie Sauvage dans l'Age de la Cybernétique
Le CTA a fait paraître dernièrement une vidéo éducative sur la technologie CyberTracker. La vidéo est un élément d’un paquet pédagogique, destiné à promouvoir les bonnes pratiques en matière de production, de gestion, d’analyse et de communication de l’information géospatiale. D’une durée de 8 minutes, la vidéo est disponible en anglais, français, espagnol et met l’accent sur de nombreux domaines dans lesquels cette technologie peut être utilisée à des fins de développement et de conservation de l’environnement.
CyberTracker est un logiciel en libre accès (open source) mis au point en Afrique du Sud par l’ONG CyberTracker Conservation avec, à l’origine, le soutien financier de la Commission Européenne. Il peut être installé sur tout appareil portable équipé d’un GPS – un Assistant numérique personnel (PDA) ou un Smartphone, par exemple – et permet de recueillir des données géoréférencées avec des annotations numériques détaillées. C’est un moyen extrêmement efficace de stocker de grandes quantités d’observations géocodées faites sur le terrain, à une vitesse et avec un niveau de précision et de détail inédits. CyberTracker permet aux utilisateurs de personnaliser l’interface pour mieux l’adapter à leurs besoins de collecte de données. Les écrans sont configurés de manière à pouvoir combiner du texte et des icônes, pour garantir ainsi une efficacité et une personnalisation optimales. L’interface icônes de l’application CyberTracker a été initialement conçue pour les pisteurs qui ne pouvaient ni lire ni écrire. Aujourd’hui, tous les utilisateurs – y compris scientifiques et écologistes – mettent à profit cette interface icônes parce qu’elle permet de saisir les données beaucoup plus rapidement.
Saturday, October 17, 2009
Educational Video ob CyberTracker - Tracking in the Cyber Age
The CTA recently released an educational video on CyberTracker technology. The video has been produced in the context of the development of a training kit aimed at supporting the spread of good practice in generating, managing, analysing and communicating spatial information. This 8-min video on CyberTracker covers a number of uses to which geospatial information technology (GIT) can be put to work in the contexts of development and conservation.
CyberTracker is an open-source software developed in South Africa by the Cybertracker Conservation with financial support initially provided of by the European Commission. It can be installed on a GPS-enabled handheld device such as a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) or a Smartphone to collect geo-referenced data with detailed digital notation. It is a highly efficient way to gather large quantities of geo-coded field observations at a speed and level of detail not possible before. CyberTracker allows users to customise the interface to meet data collection needs. Screen designs can combine text and icons to optimise efficiency and customisation. The CyberTracker icon interface was originally designed for trackers who could not read or write. Nowadays all users including scientists and conservationists benefit from the icon-based interface because it enables significantly faster data entry.
Saturday, October 10, 2009
Participatory 3D Modelling: a Review ...
Participatory 3D Modelling (P3DM) is a community-based mapping method which integrates local spatial knowledge with data on elevation of the land and depth of the sea to produce stand-alone, scaled and geo-referenced relief models. Essentially based on local spatial knowledge, land use and cover, and other features are depicted by informants on the model by the use of pushpins (points), yarns (lines) and paints (polygons). On completion, a scaled and geo-referenced grid is applied to facilitate data extraction or importation. Data depicted on the model are extracted, digitised and plotted. On completion of the exercise the model remains with the community. More information on the method are available at iapad.org



